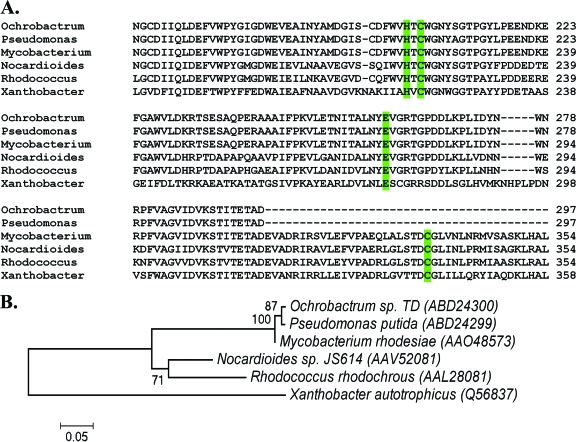
FIG. 3.
(A) Multiple-sequence alignment of EaCoMT protein sequences, performed using ClustalW (62). (B) Evolutionary relationships of six taxa. The evolutionary history was inferred using the neighbor-joining method (54). The bootstrap consensus tree, inferred from 500 replicates (20), is taken to represent the evolutionary history of the taxa analyzed (20). Branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in <50% of bootstrap replicates are collapsed. The percentages of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (500 replicates) are shown next to the branches (20). The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Poisson correction method (73) and are given as numbers of amino acid substitutions per site. All positions containing alignment gaps and missing data were eliminated only in pairwise sequence comparisons. Phylogenetic analyses were conducted in MEGA4 (57).