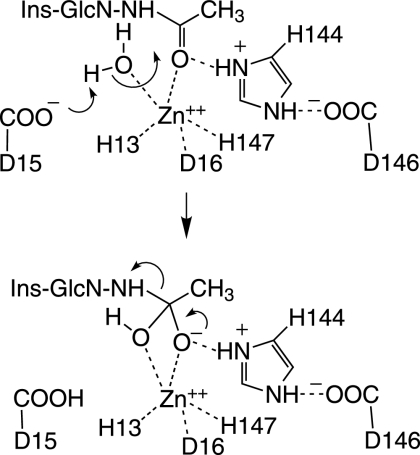
FIG. 4.
Proposed mechanism for the M. tuberculosis deacetylase MshB (71). The active site is formed with Asp15, His13, and His147 coodinating a Zn ion required for catalysis and protein stability. The active-site Zn also polarizes the acetyl carbon-oxygen bond of bound GlcNAc-Ins for attack by a hydroxyl ion generated from water by protonation of Asp15. The forming acetate is hydrogen bonded to His144 or Asp15 to complete the hydrolysis.