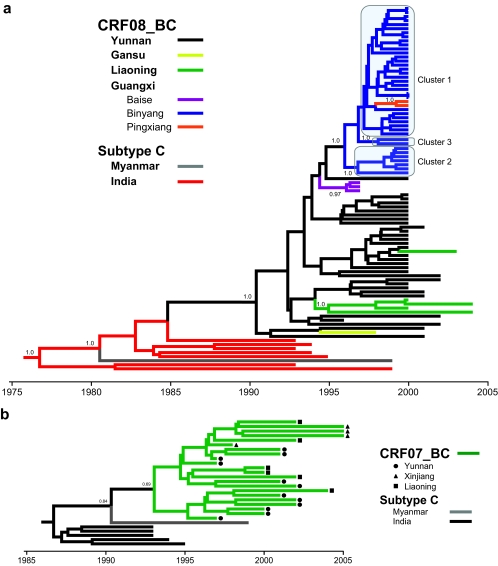
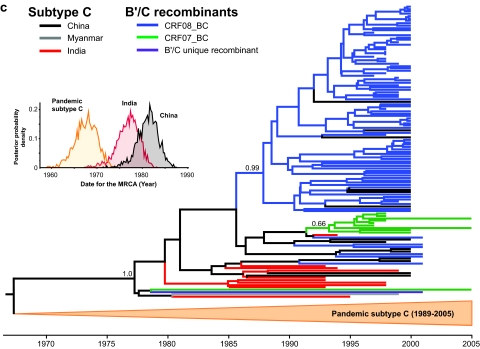
FIG. 1.
Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic analyses of HIV-1 CRF08_BC, CRF07_BC, and subtype C in China. (a) Phylogenetic reconstructions of CRF08_BC gag-pol genes (HXB2 nucleotides 1918 to 2852) isolated from HIV-1 patients in the Yunnan (Kunming, Honghe, and Wenshan), Gansu, Liaoning (Shenyang), and Guangxi (Baise, Binyang, and Pingxiang) regions of China. (b) Maximum clade credibility trees of the HIV-1 CRF07_BC sequences from Yunnan, Xinjiang, and Liaoning provinces, based on the gag gene (HXB2 nucleotides 790 to 1218). (c) The env (HXB2 nucleotides 6984 to 7328) phylogeny of subtype C, CRF08_BC, CRF07_BC, and a B′/C unique recombinant form isolated from China. Ancestral relationships are estimated using PAUP*, version 4.0 beta (40), and BEAST, version 1.4 (7). Subtype C of Indian origin, thought to be the putative parent of both CRF08_BC and CRF07_BC (19, 20), is also included. The CRF08_BC gag-pol and CRF07_BC gag tree branches are colored according to their respective geographical locations while the env tree branches show the respective HIV-1 subtype/CRF. Posterior probabilities greater than 0.5 are shown at their respective nodes.