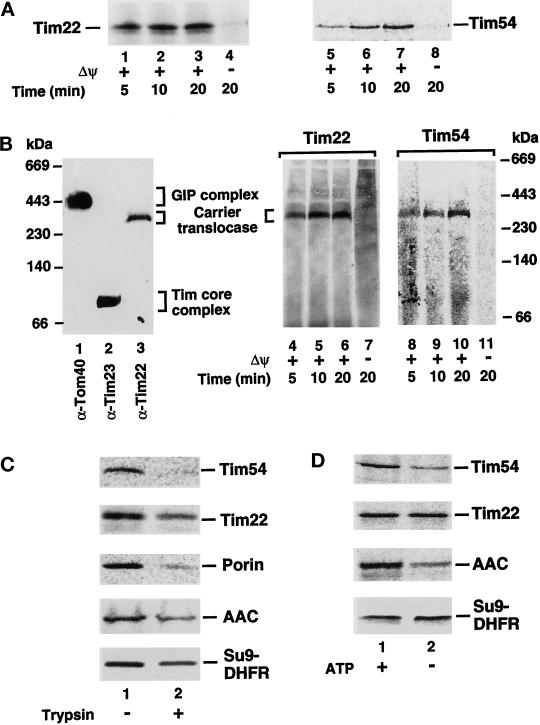
Figure 1.
Biogenesis of Tim22 and Tim54. (A) Import kinetics of Tim22 and Tim54. 35S-labeled Tim22 and Tim54 preproteins were imported into mitochondria for different times in the presence (lanes 1–3, 5–7) or absence (lanes 4 and 8) of a membrane potential (Δψ) as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. After import, mitochondria were treated with 50 μg/ml proteinase K and subjected to SDS-PAGE. (B) Assembly of Tim22 and Tim54 into the carrier translocase. Mitochondria were solubilized in digitonin-containing buffer and subjected to blue native gel electrophoresis. The gel was blotted, and lanes were immunodecorated with antibodies specific for Tom40 (lane 1), Tim23 (lane 2), or Tim22 (lane 3). For lanes 4–11, Tim22 and Tim54 preproteins were imported into mitochondria as in A, and mitochondria were electrophoresed on blue native PAGE as above. (C) The import of Tim54 and Tim22 requires surface receptors. Mitochondria were pretreated with 20 μg/ml trypsin for 20 min, before inactivation with a 30-fold excess of trypsin inhibitor (lane 2). For control samples (lane 1), trypsin-inhibitor was added to mitochondria before the addition of trypsin. 35S-labeled Tim22 and Tim54 preproteins were subjected to mitochondrial import as well as 35S-labeled porin, AAC, and Su9-DHFR preproteins, which served as controls. Samples were treated with proteinase K before SDS-PAGE analysis. (D) The import of Tim22 and Tim54 show differential requirements for ATP. 35S-labeled Tim22, Tim54, AAC, and Su9-DHFR in reticulocyte lysates were depleted of ATP. Preproteins were imported into mitochondria in the presence (lane 1) or absence of added ATP. In lane 2, mitochondria were additionally blocked in the export of ATP from the matrix according to Glick (1995). Samples were treated with proteinase K before SDS-PAGE analysis. Radiolabeled proteins were detected by storage phosphorimage cassette technology.