FIG. 5.
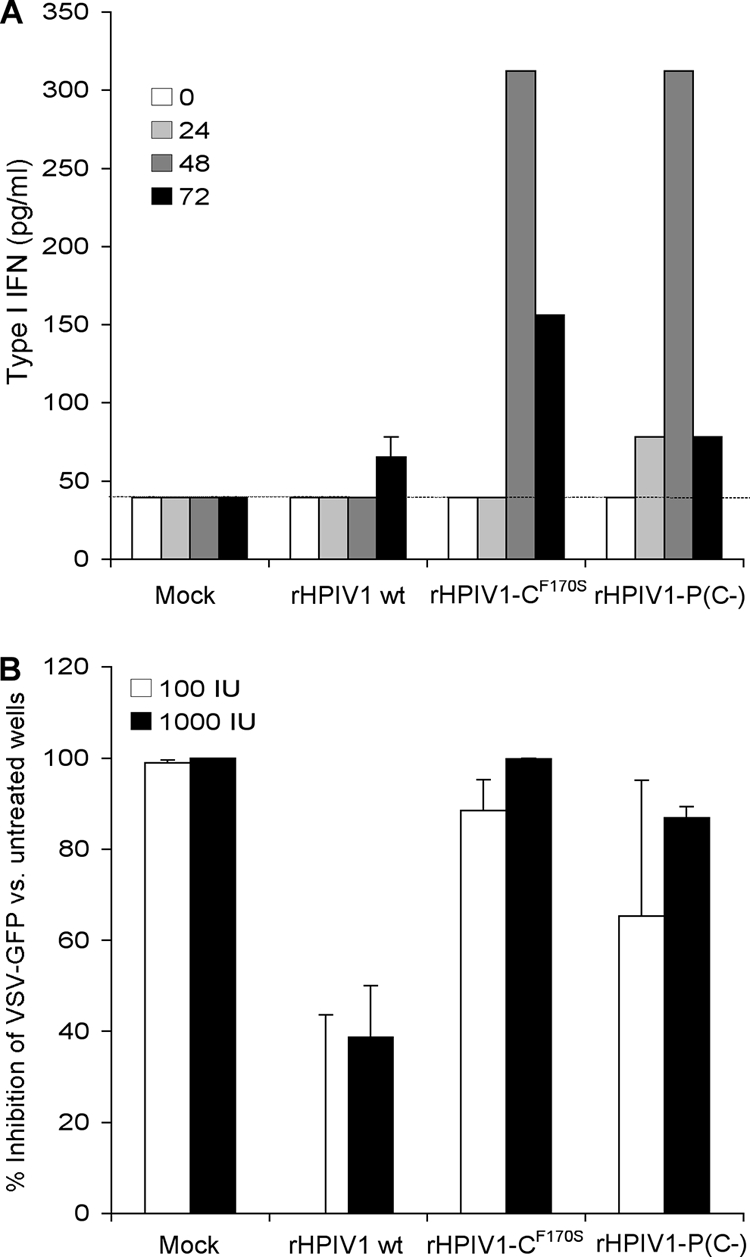
Wt rHPIV1, but not rHPIV1-P(C−), inhibits type I IFN induction and signaling. (A) Induction of type I IFN. A549 cell monolayers were either mock infected or infected with wt rHPIV1, rHPIV1-CF170S, or rHPIV1-P(C−) at an MOI of 5 TCID50/cell. Aliquots of the overlying medium were taken at 0, 24, 48, and 72 h p.i. and assayed on fresh cells for the ability to inhibit infection and GFP expression by VSV-GFP as measured with a phosphorimager. IFN concentrations were determined by comparison with a standard curve prepared in parallel with an Avonex IFN-β standard and are expressed in pg/ml ± SE based on the results for triplicate samples. The lower limit of detection was 39.1 pg/ml (dashed line). (B) Type I IFN signaling. Vero cells in six-well plates were infected with the indicated rHPIV1 at an MOI of 5 TCID50/cell and incubated for 24 h. Cells were then left untreated or were treated with 100 or 1,000 IU/ml IFN-β (one well per treatment per virus) for 24 h. The cells were then infected with VSV-GFP and incubated for 48 h. The VSV-GFP foci were visualized by using a phosphorimager and counted. The graph represents the percent inhibition of VSV-GFP replication in IFN-β-treated versus untreated cells based on the results of two independent experiments. Error bars show SE.
