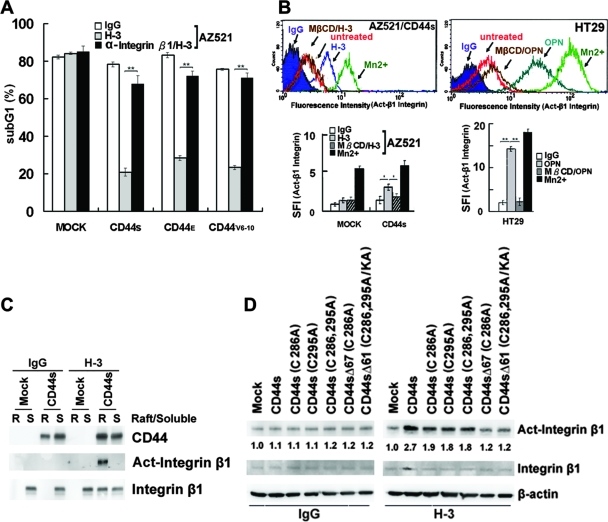
FIG. 4.
CD44-mediated survival signal is dependent on integrin activation in lipid rafts. (A) AZ521/Mock and various AZ521/CD44 cell clones were treated with H-3 MAb or control IgG in the presence and absence of blocking Ab against integrin β1, followed by UV irradiation, and apoptosis was measured by flow cytometric analysis of sub-G1 fractions as described in Materials and Methods. (B) AZ521/Mock, AZ521/CD44S, and HT29 cells were incubated without (untreated) and with H-3 MAb or OPN as described in the Fig. 1 legend. After fixation, cells were stained with MAb against integrin β1 (HUTS-21) or an isotype IgG, labeled with Alexa 488-conjugated secondary Ab, and subjected to flow cytometric analysis. Cells incubated with 2 mM MnCl2 for 30 min at 37°C were included to serve as a positive control. In some experiments, cells were pretreated with 5 mM MβCD for 15 min prior to H-3 MAb treatment. In the histograms, the y axis represents the cell numbers that were stained with Abs in each logarithmic scale of fluorescence amplifier. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments, and a representative histogram is shown. The specific fluorescence index (SFI) was calculated as the ratio of the mean fluorescence value obtained with the specific Ab and the isotype control Ab. Data from three separate experiments are presented as means ± standard deviations in the bar graph. (C and D) Integrin activation upon engagement of CD44. AZ521/Mock and individual AZ521/CD44S cell clones were incubated with H-3 MAb or control IgG for 1 h. In panel C, Triton X-100-soluble (S) and -insoluble raft (R) fractions were isolated, followed by Western blot analyses of CD44, integrin β1, and activated integrin β1. In panel D, total cell lysates were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis of activated integrin β1.