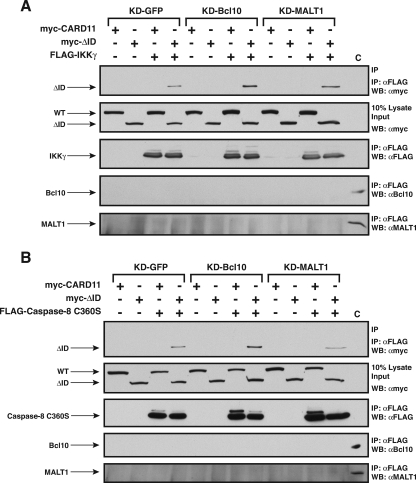
FIG. 12.
Effect of Bcl10 and MALT1 knockdown on the association of the ΔID with IKKγ and caspase-8 C360S in HEK293T cells. The KD-GFP, KD-Bcl10, and KD-MALT1 cell lines were transfected with expression vectors for the wild-type CARD11 or the ΔID in the absence (−) or presence (+) of expression vectors for FLAG-tagged IKKγ or caspase-8. Anti-FLAG immunoprecipitations were performed as described in Materials and Methods. In panel A, transfections included 800 ng of expression vector for IKKγ where indicated. To achieve approximately equivalent expression of wild-type and ΔID CARD11 variants in each cell line, the following amounts were used, from left to right (in ng): 100 WT, 200 ΔID, 100 WT, and 200 ΔID (for the KD-GFP cells); 200 WT, 400 ΔID, 100 WT, and 400 ΔID (for KD-Bcl10 cells); 200 WT, 400 ΔID, 100 WT, and 400 ΔID (for KD-MALT1 cells). In panel B, where indicated, transfections included 100 ng of expression vector for wild-type CARD11 and 1,000 ng of expression vector for caspase-8. To achieve approximately equivalent expression of the ΔID variant in each cell line, 200 ng of ΔID expression vector was used in the KD-GFP line, and 400 ng was used in the KD-Bcl10 and KD-MALT1 lines. The panels show the contents of the immunoprecipitate and lysate input developed with the indicated primary antibodies. In the control lane (C), the equivalent of 5% of the lysate input from the KD-GFP sample was resolved so as to provide a positive control for the Western blot (WB) analysis of the immunoprecipitates for the presence of Bcl10 and MALT1. WT, wild type; α, anti; IP, immunoprecipitation.