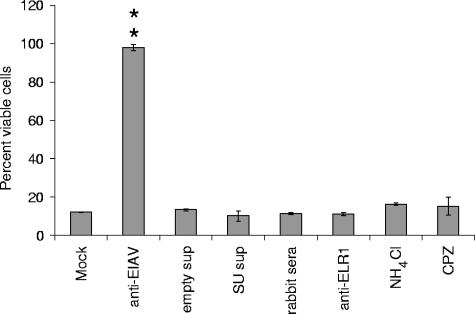
FIG. 6.
Interference with ELR1-EIAV interactions does not inhibit EIAVvMA-1c superinfection-dependent cell killing. ED cells were treated with inhibitors of ELR1-dependent entry at concentrations previously shown to inhibit 90% of EIAVMA-1 infectivity. The treated cells were infected with EIAVvMA-1c, and 4 days after infection the cells were assayed for viability. Data represent the means and standard errors of the means from three separate experiments performed in triplicate. Anti-EIAV, 1:60 dilution of equine anti-EIAV serum 2085; control sups, 100 μl of supernatant from 293T cells; WT EIAV SU sups, 100 μl of supernatant from codon-optimized SU-transfected 293T cells; normal rabbit serum, 1:60 dilution of normal rabbit serum; anti-ELR1, 1:60 of rabbit anti-ELR1 antiserum; NH4Cl, 30 mM ammonium chloride; CPZ, 20 μg/ml of chlorpromazine. **, P < 0.001.