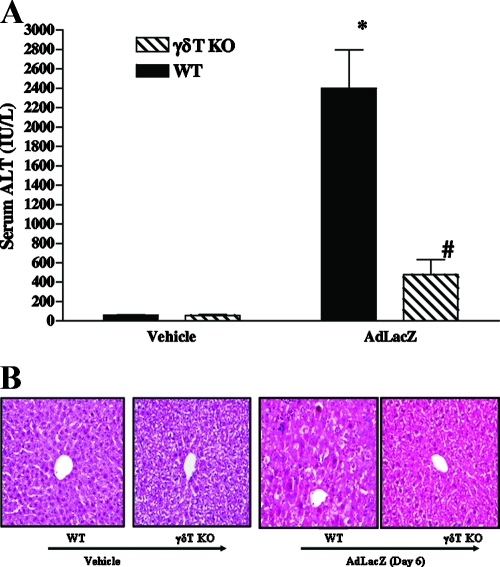
FIG. 3.
Effects of γδT-cell deficiency on acute liver inflammation and injury in AdLacZ-infected mice. WT and γδT-cell KO mice were infected with AdLacZ or vehicle for 6 days. (A) Serum samples were obtained for the determination of ALT levels. All results are presented as means ± SEM (n = 6 mice per group; *, P ≤ 0.05 versus all vehicle-treated controls; #, P ≤ 0.05 versus AdLacZ-infected WT mice). (B) Photomicrograph of H&E-stained representative liver sections depicting diffuse and severe acute hepatic injury with swelling of the hepatocytes, obliteration of the sinusoid spaces, hepatocellular necrosis, and numerous acidophilic bodies in AdLacZ-infected WT mice compared to the minimal distortion of lobular architecture and absence of inflammatory cell infiltrates in liver sections from γδT-cell KO mice after 6 days of AdLacZ infection. Original magnification, ×200. In contrast, H&E-stained liver sections from vehicle-treated WT and γδT-cell KO mice were normal.