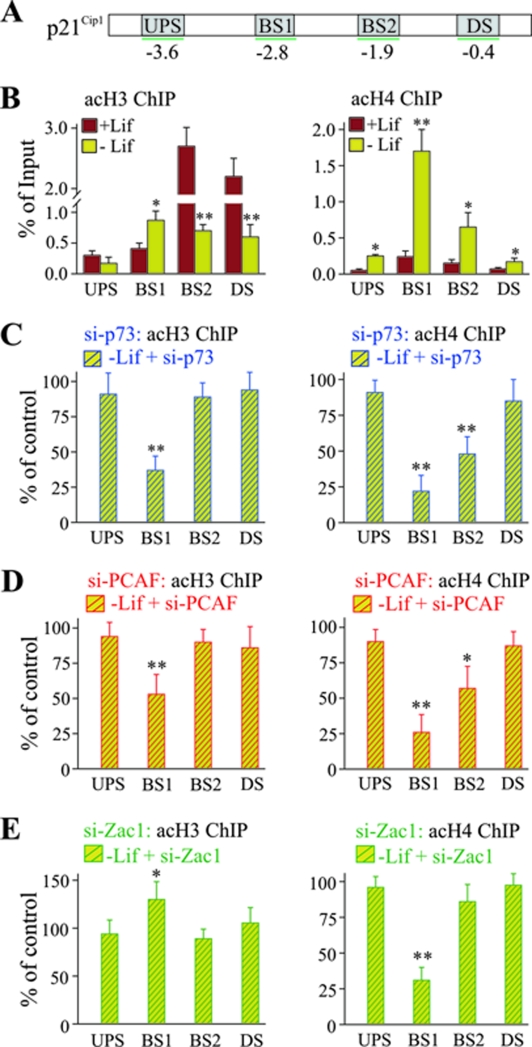
FIG. 11.
Zac1 induces a selective switch of PCAF activity in vivo. (A) Scheme of the p21Cip1 promoter, as described in the text. (B) ChIP analysis of pan-acetylated histones H3 or H4 at the p21Cip1 promoter. ChIP assays were conducted in the presence (+Lif) or absence (-Lif) of Lif for 3 days. Lif withdrawal causes an overall decrease of histone H3 acetylation. In contrast, histone H4 acetylation strongly increases at the distal p73 DNA-binding site. (C to E) ChIP analysis (as described in the text) following control or factor-specific siRNA treatments for p73 (C), PCAF (D), or Zac1 (E) on day 1 of Lif withdrawal. The cells were harvested for ChIP experiments 2 days later. The values for control siRNA treatments were set to 100%. The knockdown of p73 concomitantly reduced histone H3 and H4 acetylation at the distal p73 DNA-binding site (C), whereas the knockdown of PCAF preferentially affected histone H4 acetylation (D). In contrast, the knockdown of Zac1 significantly increased histone H3 acetylation, while histone H4 acetylation was strongly reduced (E). (B to E) P values were calculated by Student's t test for differences with versus without Lif or control versus factor-specific siRNA. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. UPS, upstream promoter region; DS, downstream promoter region; BS1, distal DNA-binding site; BS2, proximal DNA-binding site; acH3, acetylated H3; acH4, acetylated H4.