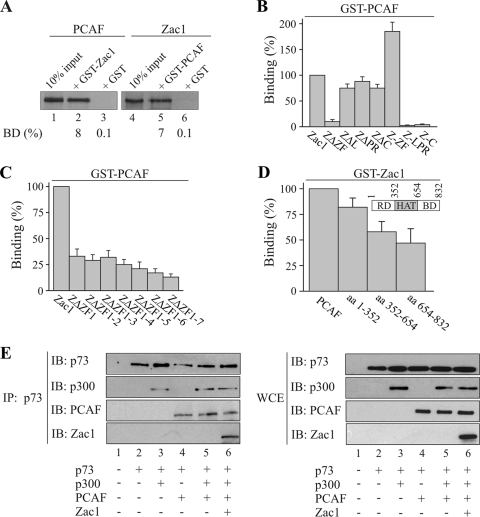
FIG. 6.
Zac1 binds PCAF in a complex with p300 and p73. (A to D) GST pull-down assays. (A) Adjusted amounts of GST-Zac1, GST-PCAF, or GST alone were incubated with equal amounts of in vitro translated Zac1 or PCAF. The fraction of the input (100%) bound by each GST protein [BD (%)] is indicated. (B) Equal amounts of in vitro-translated Zac1 proteins containing deletions of the zinc-finger (ZΔZF), linker (ZΔΖF), proline-rich (ZΔPR), or C-terminal (ZΔC) domain were each incubated with GST-PCAF or GST alone. Additionally, equal amounts of the isolated zinc-finger (Z-ZF), linker-proline-rich (Z-LPR), or C-terminal (Z-C) domains were each incubated with GST-PCAF or GST alone. Binding (%) by Zac1 is set to 100%. Zac1's zinc finger domain appears necessary and sufficient for binding to PCAF. (C) Equal amounts of in vitro-translated Zac1 proteins containing progressive deletions of individual zinc fingers were incubated each with GST-PCAF or GST alone. Binding (%) by Zac1 is set to 100%. ZF1 is strongly involved in PCAF binding. (D) Equal amounts of in vitro-translated PCAF proteins containing the amino-terminal regulatory domain (RD), the central HAT domain, or the carboxyl-terminal bromo domain (BD) were incubated with GST-Zac1 or GST alone. The inset schematically depicts the localization of these domains. The binding (%) of PCAF was set to 100%. Zac1 equally binds across different domains of PCAF. (E) Coimmunoprecipitation assays. p73 (0.5 μg), p300 (5 μg), PCAF (1 μg), and Zac1 (0.25 μg) were transfected into Saos-2 cells, as shown in the scheme. Left panel, IP were performed with the anti-p73 antibody using 1 mg cell lysate. Immunoprecipitates were blotted and tested with the indicated antibodies. p73 binds Zac1 in a complex with p300 and PCAF. Right panel, WCE of the same transfections were immunoblotted and tested with the indicated antibodies.