Figure 1.
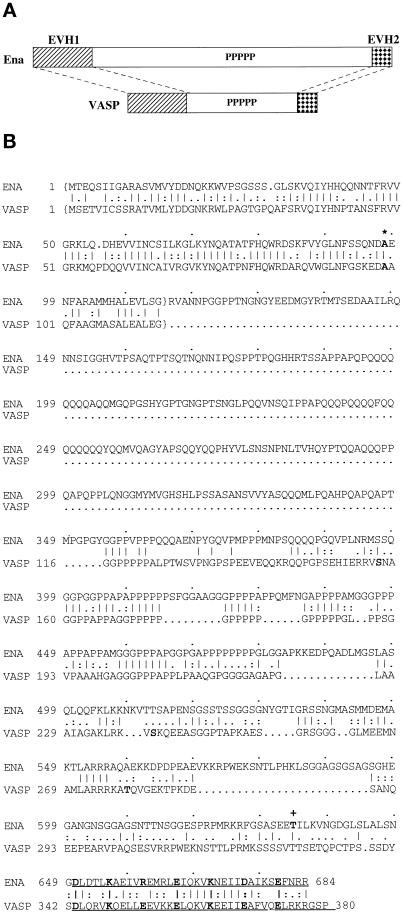
Ena and VASP have structural domain and sequence similarity, and the ena 210 and ena 23 mutations map to these regions of similarity. (A) Comparison of the overall structure and structural domain organization of Ena and VASP. The conserved EVH1 domain (hatched box) and EVH2 domain (checked box) are separated by a central domain of variable length, which contains a region rich in prolines. (B) Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequences and sequence motifs of Drosophila Ena and human VASP. The central regions of both Ena and VASP have multiple polyproline motifs. The C-terminal 35 amino acids contain a mixed charge cluster containing a charged residue at every fifth position (marked in bold). The conserved alanine that is altered in ena 210 mutants is in bold and marked with an asterisk. The EVH1 domains are enclosed in brackets, and the EVH2 domain is underlined. The location of the stop codon in ena23 is marked by a plus sign. Sequence alignment was generated using the Genetics Computer Group (Madison, WI) BestFit program. Amino acid identity is indicated by vertical lines, and similarity is indicated by dots.