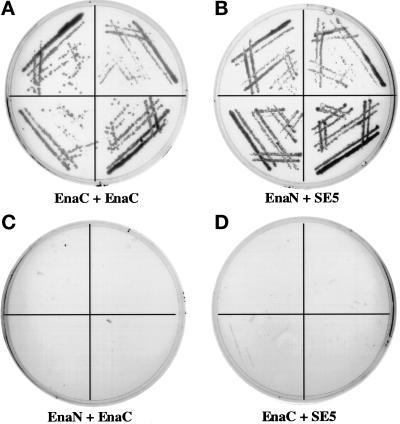
Figure 6.
Interaction of the Ena EVH2 domain with the C-terminal 243 amino acids of Ena in the yeast two-hybrid system. The first 235 amino acids of Ena (GAL4DB-Ena1–235) and last 243 amino acids of Ena (GAL4DB-Ena441–684) were fused to the sequence encoding the GAL4 DNA-binding domain in the pAS1-CYH2 vector. These two constructs were cotransformed with GAL4AD-Ena628–684, a clone in which amino acids 628–684 of Ena are fused to the sequence encoding the GAL4 activation domain and that was isolated in a yeast two-hybrid screen using the C terminal 243 amino acids of Ena as bait. Four independent colonies from each of the cotransformations were spread on medium lacking histidine and analyzed for growth. GAL4DB-Ena441–684 containing the C-terminal region of the Ena protein can interact with GAL4AD-Ena628–684 (A, EnaC + EnaC), whereas GAL4DB-Ena1–235 cannot (C, EnaN + EnaC). As a control, GAL4DB-Ena1–235 and GAL4DB-Ena401–684 were also tested for their ability to interact with GAL4AD-SE5, a clone identified from the same larval library as GAL4AD-Ena628–684 by its ability to interact with GAL4DB-Ena1–235. As expected, GAL4DB-Ena1–235 can interact with GAL4AD-SE5 (B, EnaN + SE5), whereas GAL4DB-Ena401–684 cannot (D, EnaC + SE5).