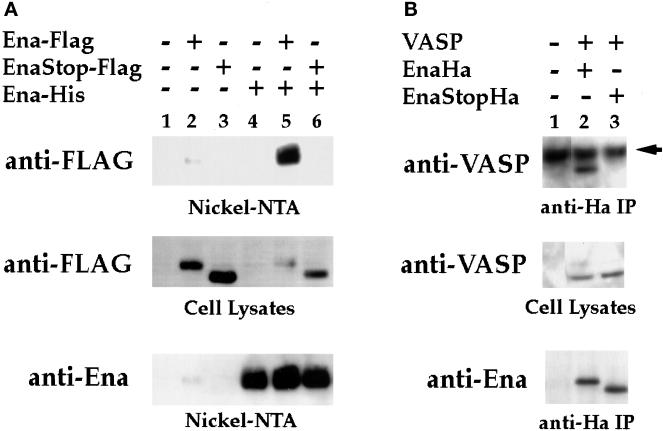
Figure 7.
The EVH2 domain mediates multimerization. (A) S2 cells were transfected with the following expression constructs: no DNA (lane 1), Ena-FLAG (lane 2), Ena K636Stop-FLAG (EnaStopFlag; lane 3), Ena-His (lane 4), Ena-FLAG + Ena-His (lane 5), and Ena K636Stop-FLAG (EnaStopFlag) + Ena-His (lane 6). Cells were lysed, and extracted proteins were purified on Ni-NTA agarose and blotted with anti-FLAG (top panel) or anti-Ena (bottom panel) antibodies. Aliquots of cell lysates representing <2% of the total protein used in the purifications were analyzed with the anti-FLAG antibody for expression of the FLAG-tagged proteins, and both the Ena-FLAG and EnaK636Stop-FLAG proteins were expressed in the presence of Ena-His (middle panel). However, only full-length Ena-FLAG copurified with the Ena-His on the nickel NTA resin (top panel, compare lanes 5 and 6). A small amount of contaminating Ena-FLAG was purified with the Nickel-NTA resin (top panel, lane 2). (B) S2 cells were transfected with the following expression constructs: no DNA (lane 1), VASP + Ena-Ha (lane 2), and VASP + Ena K636Stop-Ha (EnaStopHa; lane 3). Transfected cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with 5 μg of anti-Ha antibody. Complexes were subsequently analyzed by Western Blot with an anti-VASP antibody (top panel) or anti-Ena antibody (bottom panel). Aliquots of cell lysates representing <2% of the total protein used for the immunoprecipitations were analyzed for expression of the VASP protein with an anti-VASP antibody (middle panel). VASP was expressed in the presence of Ena-Ha and Ena K636Stop-Ha (middle panel, lanes 2 and 3), but VASP only copurified with full-length Ena-Ha in the anti-Ha IPs (compare lanes 2 and 3, top panel). The dark band present in all lanes in the top panel is the heavy-chain antibody from the anti-Ha IPs cross-reacting with the secondary antibody of the Western blot (arrow).