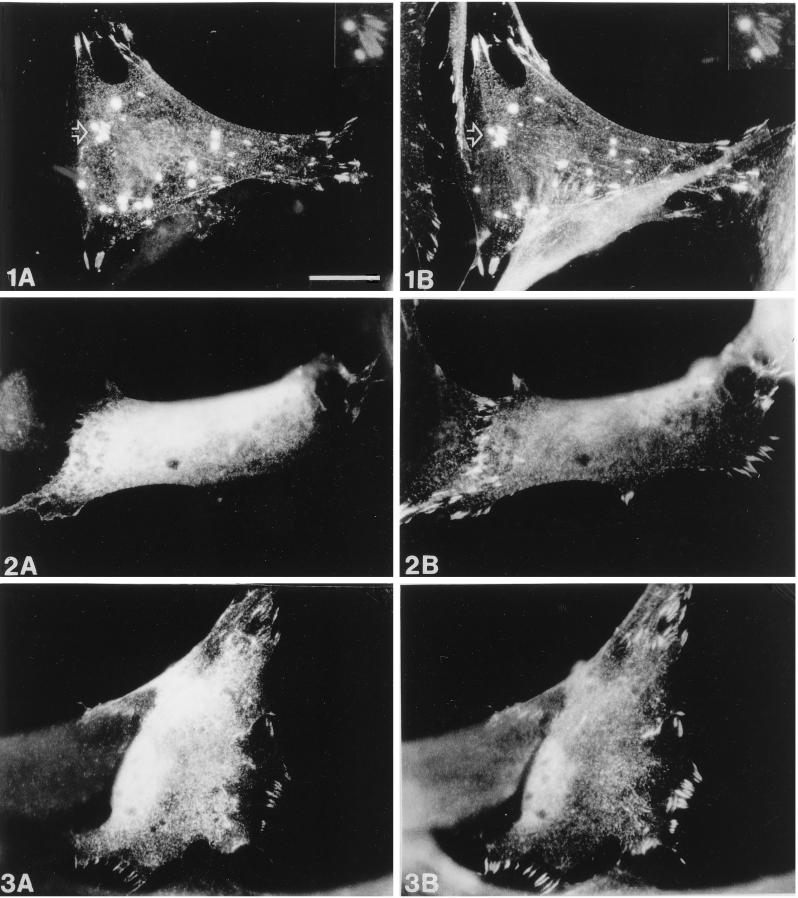
Figure 9.
Comparison of the subcellular distribution of zyxin and wild-type or mutant Ena. Human fibroblasts were transiently transfected with pCMV/Ena (1), pCMV/EnaA97V (2), or pCMV/EnaK636Stop (3) and processed for double-label immunofluorescence microscopy. Ena staining is shown in A, staining of endogenous zyxin in B. After transfection of wild-type Ena (1A and 1B), colocalization of both Ena and zyxin is found in focal contacts, on microfilaments and in spot-like structures. A magnification of the area indicated by the arrow showing two “spots” and several focal contacts is seen at the top right (insets in 1A and 1B). In contrast, EnaA97V (2A and 2B) is diffusely distributed throughout the cytoplasm and totally absent from focal contacts, which are labeled by the zyxin antibody. EnaK636Stop (3A and 3B) is also diffusely distributed in the cytoplasm but shows some residual focal contact staining, although less pronounced than that of the wild-type Ena protein. Bar in 1A, 20 μm (valid for all panels).