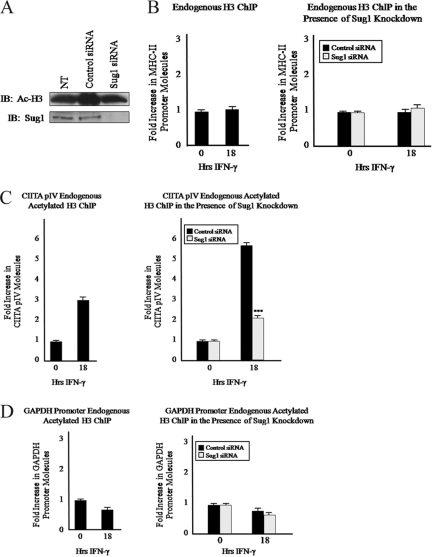
FIG. 3.
Sug1 knockdown decreases histone H3 acetylation in a promoter-specific manner. (A) Global histone H3 acetylation is unaffected by Sug1 knockdown. HeLa cells were left untreated (NT) or were transfected with either scrambled control siRNA duplexes or Sug1-specific siRNA duplexes. Lysates were subjected to IB for acetylated histone H3 (top) or for endogenous Sug1 (bottom). Results reported are data representative of three independent experiments. (B) Sug1 knockdown does not impact levels of histone H3 at the MHC-II proximal promoter. ChIP assays were carried out with HeLa cells stimulated with IFN-γ for 0 to 18 h (left) or HeLa cells transfected with scrambled siRNA control or Sug1-specific siRNA duplexes and 24 h later stimulated with IFN-γ for 0 to 18 h (right). Lysates were subjected to IP with control antibody or with antibody to endogenous histone H3. Associated DNA was isolated and analyzed via real-time PCR as described for Fig. 2B. IP values are presented as increases in the MHC-II promoter DNA relative to unstimulated histone H3 IP sample values. Control IP values were (1.15 ± 0.15)-fold. Control and histone H3 IP values represent the mean ± SEM of two or three independent experiments. (C) Sug1 knockdown decreases levels of acetylated histone H3 at the IFN-γ-inducible CIITA pIV. ChIP assays were carried out with HeLa cells stimulated with IFN-γ for 0 to 18 h (left) or HeLa cells transfected with scrambled control or Sug1-specific siRNA duplexes and 24 h later stimulated with IFN-γ for 0 to 18 h (right). Lysates were subjected to IP with control antibody or with antibody to endogenous acetylated histone H3. Associated DNA was isolated and analyzed via real-time PCR using primers spanning CIITA pIV. Real-time PCR values were normalized to the total amount of CIITA pIV DNA added to the reaction (input). Input values represent 5% of the total cell lysate. IP values are presented as increases in CIITA pIV DNA relative to unstimulated acetylated histone H3 IP sample values. Control IP values were (1.0 ± 0.1)-fold. Control and histone H3 IP values represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. (D) Sug1 knockdown does not impact levels of acetylated histone H3 at the GAPDH promoter. ChIP assays were carried out with HeLa cells stimulated with IFN-γ for 0 to 18 h (left) or HeLa cells transfected with scrambled control or Sug1-specific siRNA duplexes and 24 h later stimulated with IFN-γ for 0 to 18 h (right). Lysates were subjected to IP with control antibody or antibody to endogenous acetylated histone H3. Associated DNA was isolated and analyzed via real-time PCR using primers spanning the GAPDH promoter. Real-time PCR values were normalized to the total amount of GAPDH promoter DNA added to the reaction (input). Input values represent 5% of the total cell lysate. IP values are presented as increases in GAPDH promoter DNA relative to unstimulated acetylated histone H3 IP sample values. Control IP values were (0.75 ± 0.25)-fold. Control and histone H3 IP values represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. ***, P < 0.001 versus control siRNA.