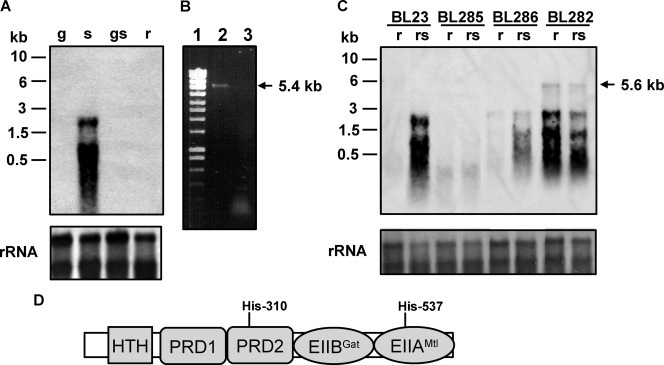
FIG. 2.
(A) Northern blot analysis performed with RNA (1 μg) isolated from L. casei BL23 (wild type) grown in MRS fermentation medium with 0.5% glucose (g), 0.5% sorbitol (s), 0.5% glucose plus 0.5% sorbitol (gs), or 0.5% ribose (r). The DNA probe spanned the promoter region of the gut operon and the 5′ end of gutF. Positions of size standard markers are indicated on the left. Stained rRNAs (23S and 16S) are shown as loading controls. (B) Agarose gel showing a RT-PCR band obtained with RNA isolated from BL23 grown on 0.5% sorbitol. Total RNA was used in RT reactions with primer gutbc4 and AMV-RT (lane 2) or without AMV-RT (lane 3). The cDNAs obtained were used in PCRs with primers gut3 and gutbc4. Ecoladder 1 (Ecogen) was used as a size standard marker (lane 1). The size of the fragment obtained is marked on the right. (C) Northern blot analysis using RNA (1 μg) isolated from L. casei BL23 (wild-type), BL282 (gutB), BL285 (gutR), and BL286 (gutM) strains. The conditions of cell cultures (0.5% ribose or 0.5% ribose plus 0.5% sorbitol [rs]) and the probe are the same as in panel A. A transcript of 5.6 kb is indicated with an arrow. Positions of size standard markers are indicated on the left. Stained rRNAs (23S and 16S) are shown as loading controls. (D) Domain organization of GutR. HTH, helix-turn-helix. Potential PTS phosphorylation sites (histidyl residues) are indicated.