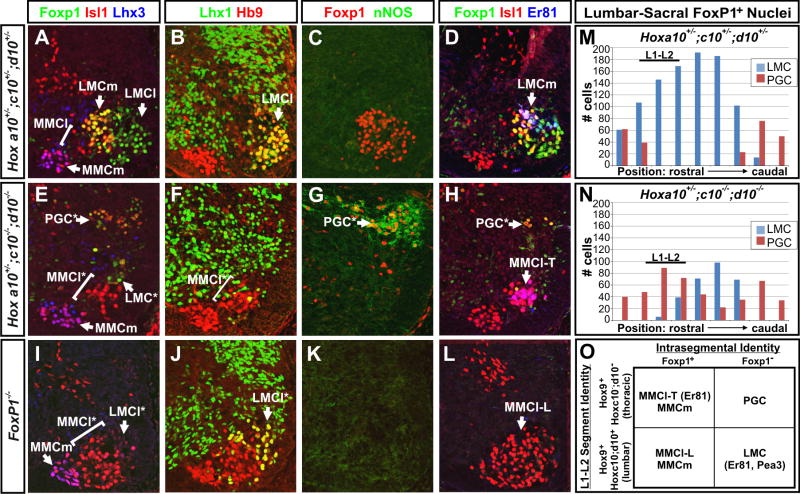
Figure 7. Cooperative functions of Foxp1 and Hox proteins are required for the formation of LMC MNs and motor pools.
(A-H) Antibody costaining analysis of lumbar (L1-L2) sections of e13.5 Hoxa10+/-; Hoxc10+/-; Hoxd10+/- 3-allele control and Hoxa10+/-; Hoxc10-/-; Hoxd10-/- 5-allele mutant embryos reveals changes in the pattern of Foxp1 expression and its abnormal association with the PGC marker nNOS rather than the LMCl marker Lhx1 and the LMCm motor pool marker Er81. Hox10 5-allele mutants also show an expansion of thoracic MMCl MNs, which express Er81 (MMCl-T), into the lumbar spinal cord.
(I-J) Analysis of motor column formation in the lumbar spinal cord (L1-L2) of age-matched Foxp1 mutant embryos. Foxp1 mutants show a reduced formation of LMCl MNs and an increased formation of MMCl that lack Er81 expression (MMCl-L).
(M-N) Distribution of Foxp1+ MNs as LMC-associated (nNOS-) and PGC-associated (nNOS+) along the rostrocaudal extent of the lumbar spinal cord of Hox10 3-allele control and Hox10 5-allele mutant litermates. Counts are representative of 3 embryos examined per genotype.
(O) Summary of the coordinate functions of Hox10 and Foxp1 in the determination of thoracic and lumbar motor columns and motor pools. In Hox10 5-allele mutants LMC MNs are transformed to a PGC fate, and lumbar MMCl MNs express the thoracic motor pool marker Er81 (MMCl-T). In Foxp1 mutants, LMC MNs are transformed into lumbar MMCl MNs that lack Er81 expression (MMCl-L). LMC MNs and LMC-associated motor pools only form in the presence of both Hoxc10/d10 and Foxp1.