Fig. 4.
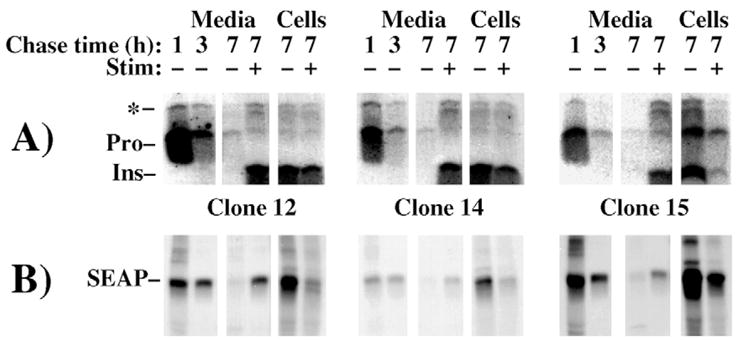
Similar handling of proinsulin and SEAP during pulse-chase examination of transfected INS-1 β-cells. Each of three independent clones expressing SEAP were pulse labeled for 30 minutes with 35S amino acids and unstimulated media were removed and replaced at 1 hour and 3 hour chase times. A final collection of medium was then performed from 3–7 hours of chase (7) under unstimulated or stimulated (Stim − or +) conditions, respectively. Secretion of insulin-containing peptides was analyzed by immunoprecipitation with anti-insulin (A, proinsulin conversion intermediates highlighted with an asterisk), whereas secretion of SEAP from the identical samples was analyzed by immunoprecipitation with anti-alkaline phosphatase (B). Note that SEAP enters and is stored within the stimulus-dependent secretory pathway, in parallel with insulin, in all clones of INS-1 cells.
