Fig. 6.
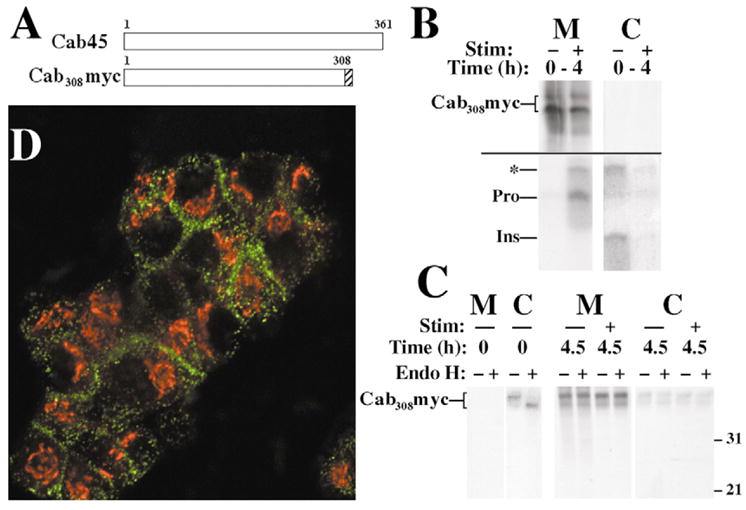
Secretion of Cab308Myc from transfected INS cells. (A) Scheme of the primary structure of Cab45 and the Cab308Myc construct. (B) Cells were pulse labeled for 30 minutes with 35S amino acids and chased continuously for 4 hours in the absence (−) or presence (+) of secretagogue (Stim). Media (M) were collected and cells lysed (C), and the samples were then analyzed by sequential immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc (upper panel) and anti-insulin (lower panel; proinsulin conversion intermediates highlighted with an asterisk). (C) Cells were labeled as in B and then either lysed immediately without chase (Time 0) or chased for 4.5 hours in the absence (−) or presence (+) of secretagogue (Stim). Media (M) were collected and cells lysed (C), and the samples were then analyzed by immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc followed by mock digestion (−) or endoglycosidase H (Endo H) digestion (+). By SDS-PAGE, Cab308Myc migrates as two bands ranging from 33 to 35 kDa. (D) Double-labeled immunofluorescence distribution of Cab308Myc in transfected INS-1 cells (using polyclonal rabbit anti-Myc, green) relative to the (Golgi) distribution of GM130 (in red).
