Figure 6. Degranulated platelets are unable to prevent thrombocytopenia-induced tumor bleeding.
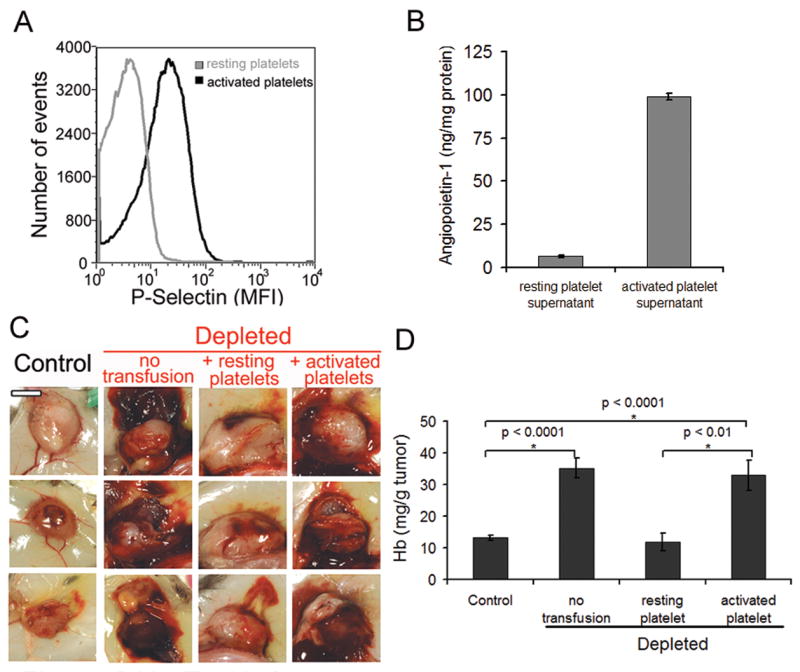
A. Degranulation of thrombin-stimulated platelets was assessed by FACS analysis of P-selectin surface expression and by B. Quantitation of angiopoietin-1 in platelet supernatants by ELISA. C. At day 8 after tumor cells implantation, mice were injected with either the control IgG (control) or the platelet-depleting IgG (depleted). A subset of mice was transfused 30 minutes prior to the induction of thrombocytopenia with tyrode buffer (no transfusion) or with 7 × 108 of either resting (resting platelets) or activated platelets (activated platelets) and subcutaneous LLC were photographed 18 hours later. Bar = 5 mm. D. Comparison of the hemoglobin content of control tumors and platelet-depleted tumors from mice transfused with either tyrode buffer, resting platelets, or activated platelets (n = 17–20).
