Abstract
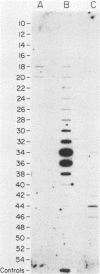
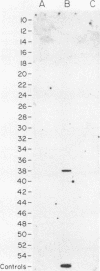
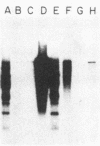
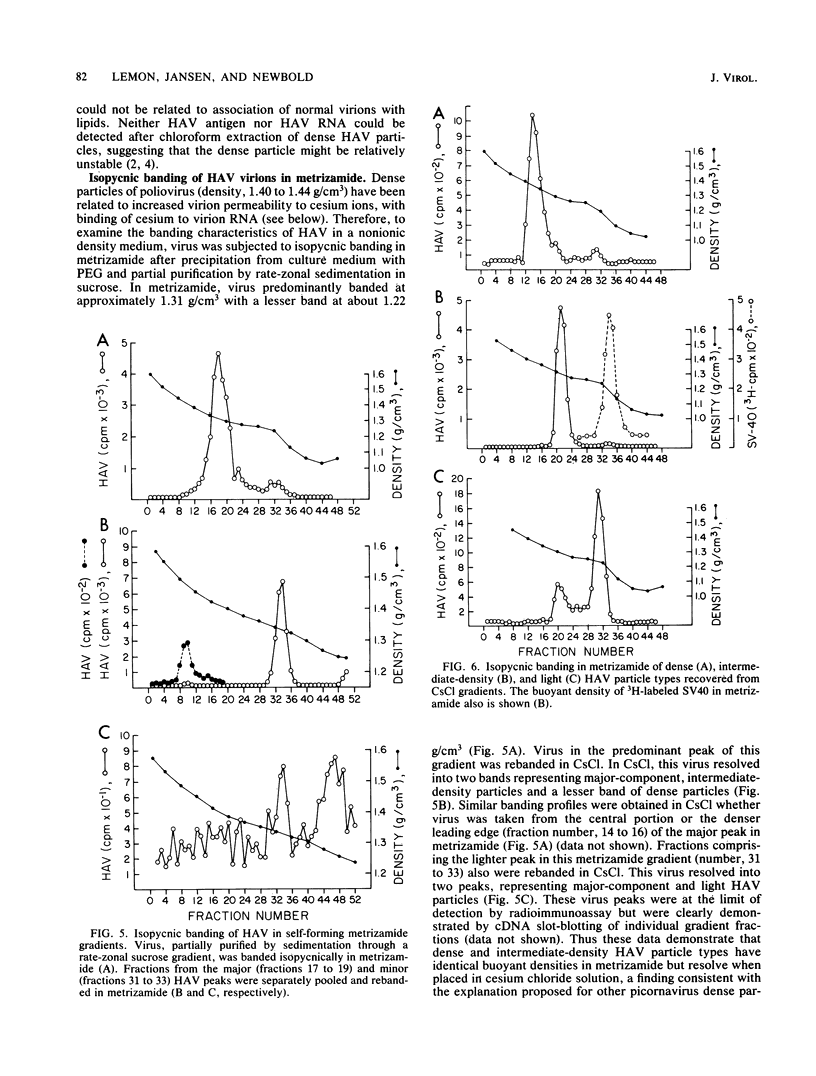
Although hepatitis A virus (HAV) released by infected BS-C-1 cells banded predominantly at 1.325 g/cm3 (major component) in CsCl, smaller proportions of infectious virions banded at 1.42 g/cm3 (dense HAV particles) and at 1.27 g/cm3 (previously unrecognized light HAV particles). cDNA-RNA hybridization confirmed the banding of viral RNA at each density, and immune electron microscopy demonstrated apparently complete viral particles in each peak fraction. The ratio of the infectivity (radioimmunofocus assay) titer to the antigen (radioimmunoassay) titer of the major component was approximately 15-fold greater than that of dense HAV particles and 4-fold that of light HAV particles. After extraction with chloroform, the buoyant density of light and major component HAV particles remained unchanged, indicating that the lower density of the light particles was not due to association with lipids. Light particles also banded at a lower density (1.21 g/cm3) in metrizamide than did the major component (1.31 g/cm3). Dense HAV particles, detected by subsequent centrifugation in CsCl, were indistinguishable from the major component when first banded in metrizamide (1.31 g/cm3). However, dense HAV particles recovered from CsCl subsequently banded at 1.37 g/cm3 in metrizamide. Electrophoresis of virion RNA under denaturing conditions demonstrated that dense, major-component, and light HAV particles all contained RNA of similar length. Thus, infectious HAV particles released by BS-C-1 cells in vitro consist of three distinct types which band at substantially different densities in CsC1, suggesting different capsid structures with varied permeability to cesium or different degrees of hydration.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binn L. N., Lemon S. M., Marchwicki R. H., Redfield R. R., Gates N. L., Bancroft W. H. Primary isolation and serial passage of hepatitis A virus strains in primate cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):28–33. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.28-33.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., Fields H. A., McCaustland K. A., Cook E. H., Gravelle C. R., Maynard J. E. Biochemical and biophysical characterization of light and heavy density hepatitis A virus particles: evidence HAV is an RNA virus. J Med Virol. 1978;2(2):175–187. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890020212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., Hornbeck C. L., Cood E. H., Maynard J. E., Gravelle C. R. CsCl banding of hepatitis A-associated virus-like particles. J Infect Dis. 1975 Mar;131(3):304–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., McCaustland K. A., Schreeder M. T., Cook E. H., Gravelle C. R., Maynard J. E. Multiple buoyant densities of hepatitis A virus in cesium chloride gradients. J Med Virol. 1977;1(3):219–226. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890010309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee N. K., Samsonoff W. A., Tuchowski C. Isolation and characterization of a membrane-bound population of group B coxsackieviruses. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):832–841. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.832-841.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N. Defective interfering (di) particles of poliovirus. Prog Med Virol. 1975;20:180–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulepis A. G., Locarnini S. A., Westaway E. G., Tannock G. A., Gust I. D. Biophysical and biochemical characterization of hepatitis A virus. Intervirology. 1982;18(3):107–127. doi: 10.1159/000149314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daemer R. J., Feinstone S. M., Gust I. D., Purcell R. H. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in African green monkey kidney cell culture: primary isolation and serial passage. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):388–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.388-393.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstone S. M., Kapikian A. Z., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H. Buoyant density of the hepatitis A virus-like particle in cesium chloride. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1412–1414. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1412-1414.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frösner G. G., Deinhardt F., Scheid R., Gauss-Müller V., Holmes N., Messelberger V., Siegl G., Alexander J. J. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in a hepatoma cell line. Infection. 1979;7(6):303–305. doi: 10.1007/BF01642154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Binn L. N., Marchwicki R. H. Radioimmunofocus assay for quantitation of hepatitis A virus in cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):834–839. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.834-839.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., LeDuc J. W., Binn L. N., Escajadillo A., Ishak K. G. Transmission of hepatitis A virus among recently captured Panamanian owl monkeys. J Med Virol. 1982;10(1):25–36. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890100105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Ferris A. A., Stott A. C., Gust I. D. The relationship between a 27-nm virus-like particle and hepatitis A as demonstrated by immune electron microscopy. Intervirology. 1974;4(2):110–118. doi: 10.1159/000149849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapoles J. E., Anderegg J. W., Rueckert R. R. Properties of poliovirus propagated in medium containing cesium chloride: implications for picornaviral structure. Virology. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Hilleman M. R. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in cell culture in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Feb;160(2):213–221. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Wolanski B. S., Miller W. J., Ittensohn O. L., McAleer W. J., Hilleman M. R. Physical, chemical and morphologic dimensions of human hepatitis A virus strain CR326 (38578). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Feb;148(2):532–539. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. J., Shirley M. W., Sangar D. V., Brown F. A high density component in several vertebrate enteroviruses. J Gen Virol. 1975 Nov;29(2):223–234. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman A. N., Dienstag J. L., Jackson D. R., Hoofnagle J. H., Gerety R. J., Purcell R. H., Barker L. F. Hepatitis A antigen particles in liver, bile, and stool of chimpanzees. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):80–84. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Frösner G. G. Characterization and classification of virus particles associated with hepatitis A. I. Size, density, and sedimentation. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):40–47. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.40-47.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Frösner G. G., Gauss-Müller V., Tratschin J. D., Deinhardt F. The physicochemical properties of infectious hepatitis A virions. J Gen Virol. 1981 Dec;57(Pt 2):331–341. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-57-2-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J. Physical map of polyoma viral DNA fragments produced by cleavage with a restriction enzyme from Haemophilus aegyptius, endonuclease R-HaeIII. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):946–953. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.946-953.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticehurst J. R., Racaniello V. R., Baroudy B. M., Baltimore D., Purcell R. H., Feinstone S. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of hepatitis A virus cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5885–5889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Hofmann L., Wurster K. G., Flehmig B. Persistent infection of human fibroblasts by hepatitis A virus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Mar;65(Pt 3):609–615. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-3-609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi-Koll U., Wiegers K. J., Drzeniek R. Isolation and characterization of 'dense particles' from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Gen Virol. 1975 Mar;26(3):307–319. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-3-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]