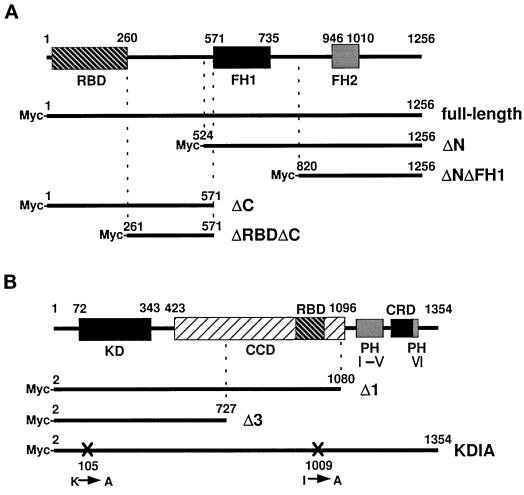
Figure 1.
Structures of ROCK, mDia, and their mutants. (A) Structural domains of mDia are schematically illustrated at the top, and full-length and four mutants are represented by the thick lines below. Numbers indicate amino acid residues of the N and C termini of each mutant. RBD, Rho-binding domain; FH1, FH domain 1; FH2, FH domain 2. (B) Structural domains of ROCK are schematically illustrated at the top, and three mutants are represented by the thick lines below. Numbers indicate amino acid residues of the N and C termini of each mutant. KD, kinase domain; CCD, coiled coil–forming amphiphatic α-herical domain; RBD, Rho-binding domain; PH, pleckstrin homology domain; CRD, cysteine-rich zinc-finger domain; X, positions of mutations with amino acid numbers.