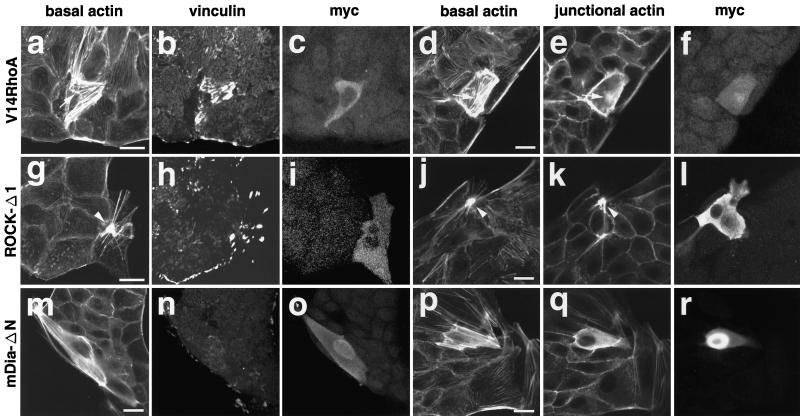
Figure 2.
Effect of the dominant active mutant of Rho, ROCK, or mDia on the actin cytoskeleton in MDCK cells. pEF-BOS-myc-V14RhoA (a–f), pCAG-myc-ROCK-Δ1 (g–l), or pEF-BOS-myc-mDia-ΔN (m–r) was microinjected into the nuclei of MDCK cells. At 10 h after the microinjection, the cells were fixed and triple stained with rhodamine-phalloidin (a, g, and m), the anti-vinculin mAb (b, h, and n), and the anti-myc pAb (c, i, and o) or double stained with rhodamine-phalloidin (d, e, j, k, p, and q) and the anti-myc mAb (f, l, and r). (a–d, g–j, and m–p) Confocal microscopic analysis at the basal levels. (e, f, k, l, q, and r) Confocal microscopic analysis at the junctional levels. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments. Bars, 10 μm. Arrows in a, d, and e indicate the sites where stress fibers coalesced in the V14RhoA-expressing cells. Arrowheads in g, j, and k indicate the sites where stress fibers coalesced in the ROCK-Δ1-expressing cells.