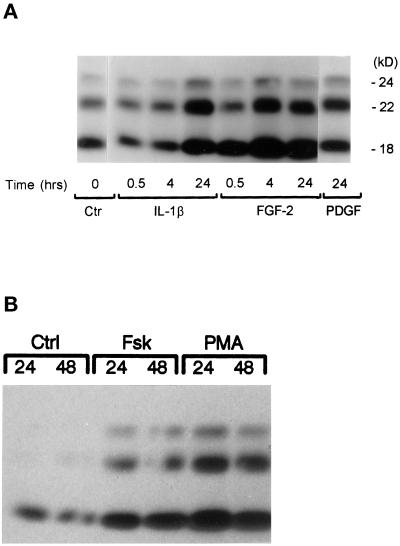
Figure 1.
Effects of growth factors (A and B), forskolin, and PMA (C) on FGF-2 content in human astrocytes: Western analysis. Subconfluent astrocytic cultures were maintained in serum-free medium containing 0.25% BSA for 24 h before the incubation with growth factors, PMA, or forskolin. Total cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. (A and B) Growth factor concentrations used (PDGFAB, 1 × 10−10 M; FGF-2, 5 × 10−10 M; IL-1β, 2.8 × 10−10 M [this Figure]; and EGF, 5.0 × 10−9 M [Figure 2]) are similar to their respective Kd values (Binger et al., 1990; Sorkin et al., 1991; Ban et al., 1993; Stachowiak et al., 1997a) and maximally or near maximally increased or FGF-2 immunoreactivity in rat (Araujo and Cotman, 1992) and human astrocytes and astrocyte proliferation (Joy et al., 1997) (our unpublished observations). Similar results were obtained in two or three independent experiments with different astrocytic cultures. (C) Western analysis of PMA- and forskolin-induced changes in FGF-2 content in human astrocytes. Subconfluent astrocytes were maintained in serum-free medium for 24 h, after which the cells were treated with forskolin (10 μM) or PMA (100 nm) for the indicated times. Control cells were incubated with 0.007% DMSO used as a vehicle for forskolin and PMA. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments.