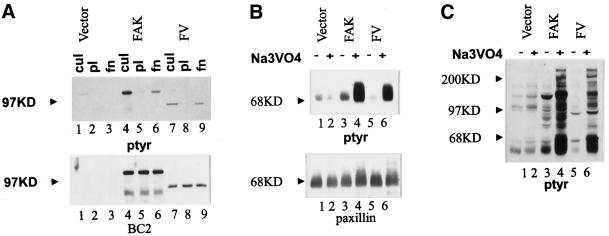
Figure 9.
The FAK/vinculin chimera functions like wild-type FAK. (A) Cells transfected with empty RCAS (lanes 1–3) and cells expressing wild-type FAK (lanes 4–6) or FAKF/V (lanes 7–9) were analyzed. Lysates of cultured cells (lanes 1, 4, and 7) or cells plated on poly-l-lysine–coated plates (lanes 2, 5, and 8) or fibronectin-coated plates (lanes 3, 6, and 9) were immunoprecipitated with BC2. The immune complexes were analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (top) or BC2 (bottom). The position of the 97-kDa molecular weight marker is shown by the arrowheads. (B and C) Control cells transfected with empty RCAS (lanes 1 and 2) and cells expressing wild-type FAK (lanes 3 and 4) or FAKF/V (lanes 5 and 6) were incubated overnight in the absence (lanes 1, 3, and 5) or presence (lanes 2, 4, and 6) of 50 μM sodium vanadate. (B) The cells were lysed, and paxillin was immunoprecipitated using a monoclonal antibody. The immune complexes were analyzed by Western blotting for phosphotyrosine (top) and for paxillin (bottom). The position of the 68-kDa molecular weight marker is indicated by the arrowheads. (C) The cells were lysed, and equivalent amounts of whole-cell lysate were directly analyzed by Western blotting for phosphotyrosine. The positions of the 200-, 97-, and 68-kDa molecular weight markers are shown by arrowheads.