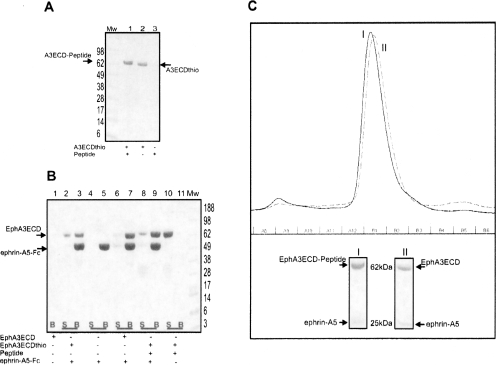
Figure 5.
The peptide ligated Eph ECD retains full biological activity. (A) The ligation efficiency is ∼99%. The EphA3 ECD α-thioester ligated with the Histidine-tagged peptide, MW = 2.1 kDa (described above) is resolved on Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE. (Lane 1) The ligated product is confirmed by the increase in MW corresponding to that of the peptide used for ligation; (lane 2) the unligated EphA3 ECD α-thioester; (lane 3) the peptide by itself is too small and is not visible on the gel. (B) The Eph ECD retains its ligand-binding activity after thiol treatment and ligation. The EphA3 ECD α-thioester obtained after thiolysis and the peptide-ligated product were mixed with the Fc-tagged ephrin-A5 ligand. The Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE shows that the recombinant ectodomain of EphA3, its α-thioester derivative, and the peptide-ligated product form a specific complex with the ephrin-A5 ligand, since they are pulled down by Protein-A Sepharose beads (B; lanes 3,7,9). Without the addition of the ephrin-A5-Fc, the peptide-ligated product of EphA3 ECD stays exclusively in the supernatant (S; lane 10). (Mw) Molecular weight marker (in kilodaltons). (C) The elution profile of the EphA3ECD/EphA3ECD-peptide in complex with the ligand ephrin-A5 resolved on a Superdex-200 10/30 gel filtration column. (I) The major peak corresponding to the ligated EphA3-ECD–Histidine-tag peptide and ephrin-A5 complex. (II) The major peak corresponding to the recombinant unligated EphA3 ECD and ephrin-A5 complex. Fraction B1, corresponding to the proteins in the major peaks of I and II, respectively, is resolved on Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel. The proteins are labeled accordingly.