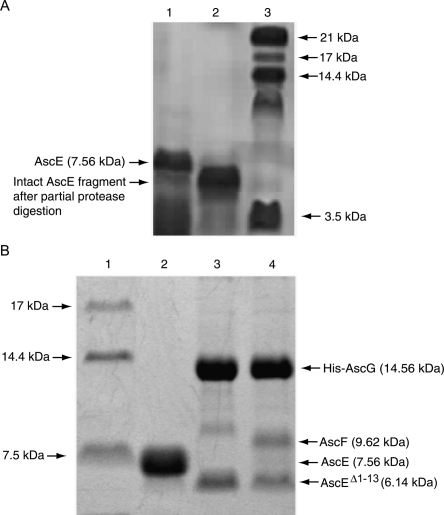
Figure 4.
SDS Tricine PAGE showing partial protease digestion of AscE and coexpression of AscEΔ1–13 with AscG or AscG and AscF. (A) Purification and partial protease digestion of the AscE dimer. (Lane 1) Purified AscE dimer; the molecular weight of the monomer is ∼7.56 kDa; (lane 2) AscE after partial protease digestion. The intact AscE fragment has a smaller molecular weight, with the N-terminal 13 residues digested as confirmed by N-terminal sequencing; and (lane 3) protein molecular weight marker. (B) Coexpression of AscEΔ1–13 with AscG or AscG and AscF. (Lane 1) Protein molecular weight marker; (lane 2) purified AscE dimer; (lane 3) coexpression of AscEΔ1–13 with AscG; (lane 4) coexpression of AscEΔ1–13 with AscG and AscF. The AscEΔ1–13 N-terminal truncation mutant (6.14 kDa) can be coexpressed and copurified with His-AscG or both His-AscG and AscF to form a soluble complex.