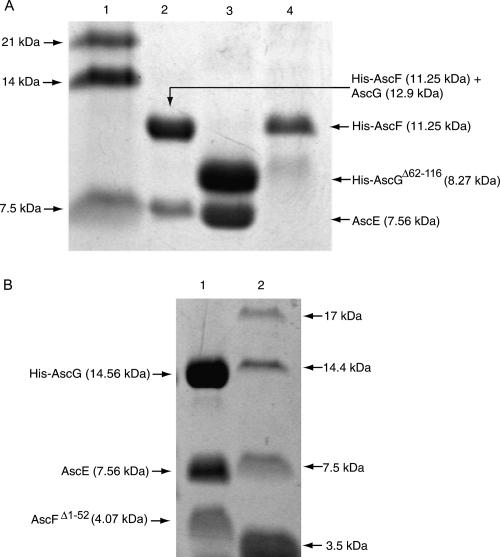
Figure 6.
Coexpression of truncated fragments of AscG or AscF in the ternary complex. (A) Coexpression of AscGΔ62–116 with AscE or AscE and AscF. (Lane 1) Protein molecular weight marker; (lane 2) coexpression of full-length AscG with AscE and His-AscF. Note that the His-tag (1.63 kDa) is located at the N terminus of AscF (9.62 kDa) resulting in a fusion protein band (11.25 kDa) that overlapped with AscG (12.9 kDa). The formation of the ternary complex is indicated by copurification of AscE (7.56 kDa). (Lane 3) The His-AscGΔ62–116 C-terminal truncation mutant (8.27 kDa) can be coexpressed and copurified with AscE as a stable soluble complex; (lane 4) coexpression of the AscGΔ62–116 C-terminal truncation mutant with AscE and His-AscF. No ternary complex can be formed, as indicated by absence of the band corresponding to AscE. (B) Coexpression of AscFΔ1–52 with AscE and AscG. (Lane 1) The AscFΔ1–52 N-terminal truncation mutant (4.07 kDa) can be coexpressed and copurified with both AscE and His-AscG to form a soluble complex; (lane 2) protein molecular weight marker.