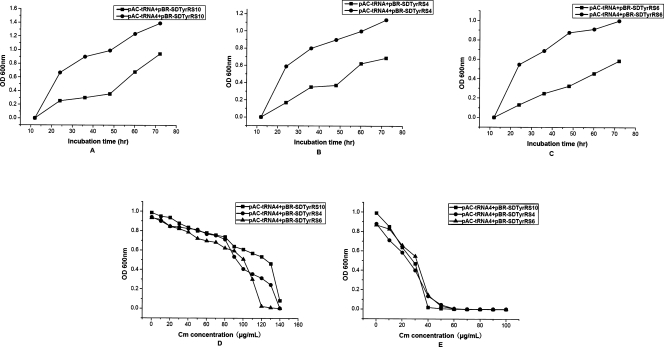
Figure 3.
After incorporation of multiple copies of plasmid-encoded Methanococcus jannaschii-derived suppressor tRNA, a series of selections based on the suppression of Asp112TAG in the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene were carried out. (A) In order to assess the efficiency of the multiple copies of suppressor tRNA, pBR-SD-TyrRS10 encoding the mutant MjTyrRS was cotransformed with pAC-tRNA and pAC-tRNA4, respectively, in DH10B cells. pAC-tRNA encoded a single suppressor tRNA and pAC-tRNA4 encoded multiple copies of suppressor tRNA. Positive selection was carried out in GMML liquid medium with 100 μg/mL chloramphenicol and p-azido-L-phenylalanine. (B) pBR-SD-TyrRS4 encoding the mutant MjTyrRS was cotransformed with either pAC-tRNA or pAC-tRNA4 in DH10B cells. Positive selection was carried out in GMML liquid medium with 100 μg/mL chloramphenicol and p-azido-L-phenylalanine. (C) pBR-SD-TyrRS6 encoding the mutant MjTyrRS was cotransformed with either pAC-tRNA or pAC-tRNA4 in DH10B cells. Positive selection was carried out in GMML liquid medium with 100 μg/mL chloramphenicol and p-azido-L-phenylalanine. (D) In concordance with the positive selections of A–C, positive selection was carried out in GMML liquid medium with various concentrations of chloramphenicol in the presence of p-azido-L-phenylalanine in order to detect the survivability with chloramphenicol. (E) Negative screen was carried out in GMML liquid medium with various concentrations of chloramphenicol in the absence of p-azido-L-phenylalanine.