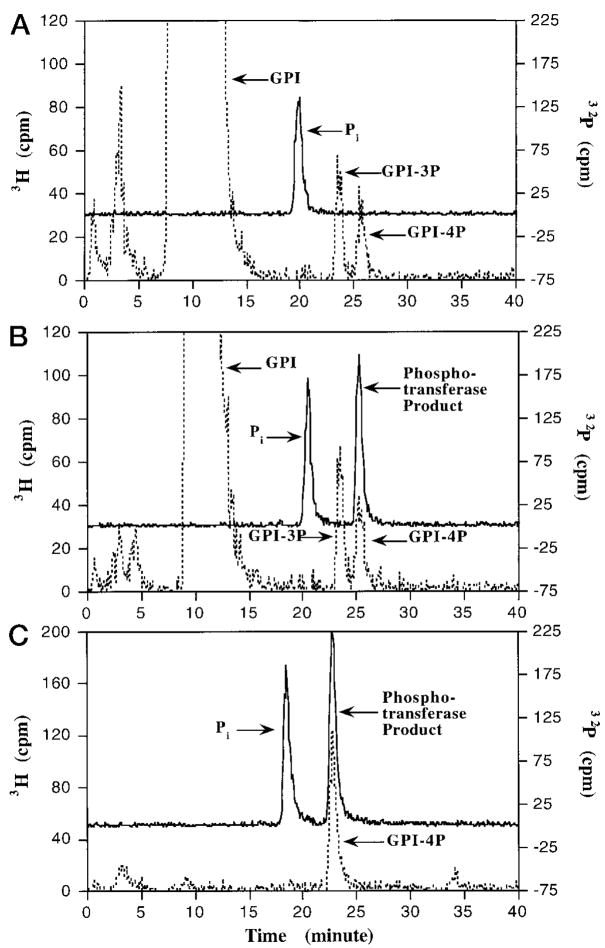
Fig. 10. Selective transfer of the 4′-phosphate group of Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA to the 4-position of the inositol moiety of PtdIns.
Three reactions (10 μl each) were carried out under standard assay conditions with 10 μM Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA (20,000 cpm/nmol) as donor. A, with enzyme (10 μg/ml heparin-agarose step) but without PtdIns; B and C, with enzyme (10 μg/ml heparin-agarose step) and with PtdIns (1 mg/ml) as the acceptor. After incubation for 40 min, internal standards consisting of PtdIns and/or its phosphorylated derivatives in 30 μl of chloroform/methanol (1:1, v/v) were added to each tube. A [1,2-3H]inositol-labeled mixture (40,000 cpm) of PtdIns and phosphorylated PtdIns derivatives isolated from yeast cells was used as the internal standard for reactions A and B, while Ptd-[2-3H]Ins-4-P (2000 cpm) was used as the internal standard for tube C. Each sample was then dried by vacuum centrifugation, followed by deacylation with methylamine and HPLC analysis of the water-soluble deacylation products (47). The elution of the 3H-labeled deacylated internal standards (broken lines) and of the 32P-labeled enzymatic reaction products (solid lines) was monitored by in-line liquid scintillation counting. The elution profiles for reactions A (no PtdIns, yeast standards), B (with PtdIns, yeast standards), and C (with PtdIns, PtdIns-4P standard) are shown in the respective panels. The peaks for internal standards (glycerophosphoinositol (GPI), glycerophosphoinositol 3-phosphate (GPI-3P), glycerophosphoinositol 4-phosphate (GPI-4P), and the 4′-phosphatase/ phosphotransferase products (32Pi and [32P]phosphotransferase product) are indicated. No 32 Pi or [32P]phosphotransferase product was seen without enzyme (not shown). The slight decrease in the retention times for the 32Pi and the GPI-4P in A versus C probably is caused by aging of the column following multiple cycles of chromatography.