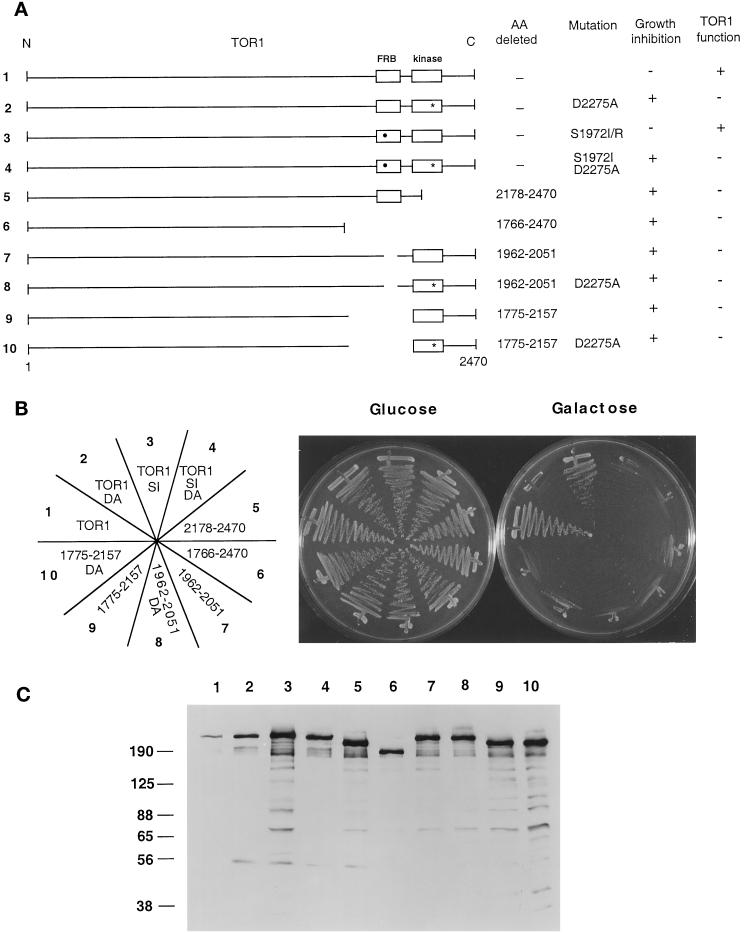
Figure 3.
TOR1 structural features required for in vivo function and overexpression toxicity. (A) Diagram of full-length TOR1 with the FRB and kinase domains depicted by open boxes. The S1972I rapamycin- resistant mutation is indicated by a black circle, and the kinase-inactive mutation D2275A by a star. The specific amino acids (AA) mutated or deleted in each mutant, and the ability of these TOR1 derivatives to inhibit growth when overexpressed, or to provide TOR1 function and complement the synthetic lethal growth defect at 39°C in a tor1 Δsrk1 mutant strain (CAY7) are indicated. N and C indicate the amino- and carboxy termini of TOR1, and 1 and 2470 indicate the positions of the first and last amino acids, respectively, of the TOR1 protein. (B) TOR1 mutants and deletion derivates were expressed in the Δtor1 strainCAY6, and the ability to inhibit growth on galactose media was tested. Cells were grown on glucose or galactose medium lacking tryptophan for 96 h at 30°C. DA and SI indicate the D2275A kinase-inactive and the S1972I rapamycin resistance mutations, respectively. The nubers on the plate designation correspond to the construct number indicated to the left in panel A. (C) TOR1 deletion mutant proteins were expressed in the Δtor1 strain CAY6 and detected by Western blot with an α-HA monoclonal antibody. Numbers above the Western blot correspond to the construct numbers listed to the left in panel A. Numbers at left indicate molecular mass in kilodaltons of marker proteins.