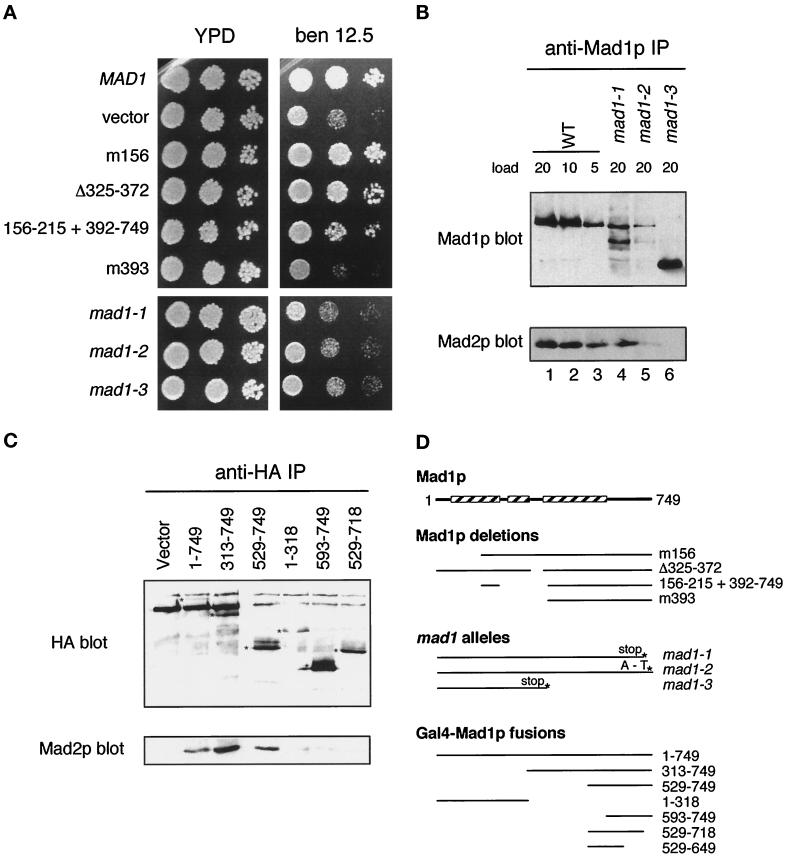
Figure 7.
The Mad2p binding domain in Mad1p. (A) mad1 constructs were assayed for their ability to complement the benomyl sensitivity of a mad1Δ strain and are compared with mad1-1, 2, and 3. Yeast strains were spotted onto plates at three dilutions and grown at 24°C. Benomyl was used at 12.5 μg/ml. (B) mad1 mutant proteins fail to co-immunoprecipitate efficiently with Mad2p. Mad1p immunoprecipitates prepared from wild-type (WT) and mutant (mad1-1, mad1-2, and mad1-3) extracts as indicated on top were immunoblotted with an anti-Mad1p (upper panel) or an anti-Mad2p (lower panel) antibody. The numbers indicate the volume (microliters) loaded of the immunoprecipitates. (C) The indicated MAD1-GAL4 DNA binding domain fusion constructs containing a hemagglutinin (HA) epitope tag were assayed for Mad2p interaction by immunoprecipitation. 16B12 (anti-HA) immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted and probed with 16B12 antibody (upper panel) or anti-Mad2p antibody (lower panel). The position of the different fusion proteins is marked with an asterisk on the anti-HA blot. (D) Summary of the different mad1 mutants, deletions, and fusion protein constructs. The boxed regions indicate the portions of Mad1p that are predicted to form a coiled coil (Hardwick and Murray, 1995).