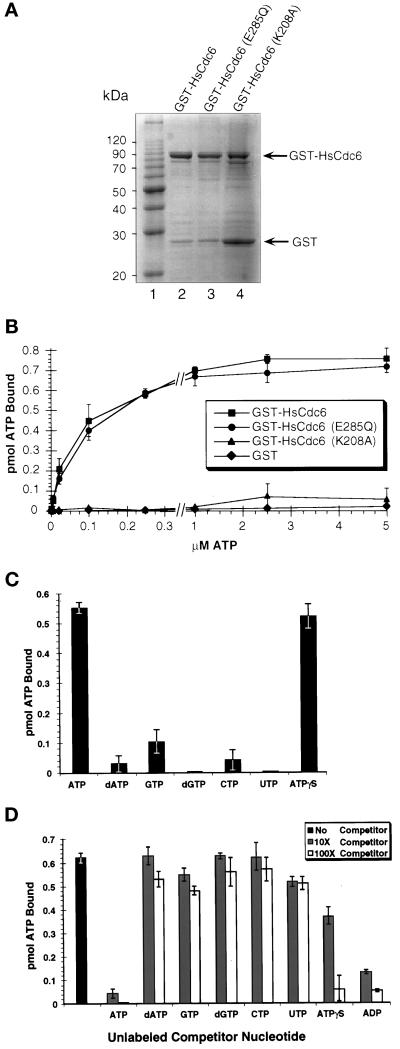
Figure 1.
Activity of wild-type and mutant HsCd6 ATP binding. (A) Purified wild-type HsCdc6 fused to GST and GST-HsCdc6 mutants with single amino acid substitutions in the Walker A or B motifs was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. (B) One pmol of GST-HsCdc6 (squares), GST-HsCdc6 (K208A) (triangles), GST-HsCdc6 (E285Q) (circles), or GST (diamonds) was incubated with increasing amounts of [α-32P]ATP for 10 min at room temperature. After gel filtration, the amount of ATP bound to the protein in the void volume was determined by scintillation counting. Recovery of protein in the void volume was consistently ∼70%. The values are averages from three separate experiments, and error bars indicate the SD. (C) One pmol of GST-HsCdc6 was incubated with the indicated radiolabeled NTP or dNTP for 10 min at room temperature. Unbound nucleotides were removed by gel filtration, and the amount of NTP or dNTP bound to GST-HsCdc6 in the void volume was determined by scintillation counting (mean of 2 separate experiments). Error bars indicate the SD. (D) GST-HsCdc6 (1 pmol) was incubated with 2.5 μM [α-32P]ATP in the absence (black bar) or presence of the indicated unlabeled competitor nucleotides in a 10-fold (hatched bars) or a 100-fold (white bars) excess. Unbound nucleotides were removed by gel filtration, and the amount of [α-32P]ATP bound to GST-HsCdc6 was determined by scintillation counting (mean of 2 separate experiments). Error bars indicate the SD.