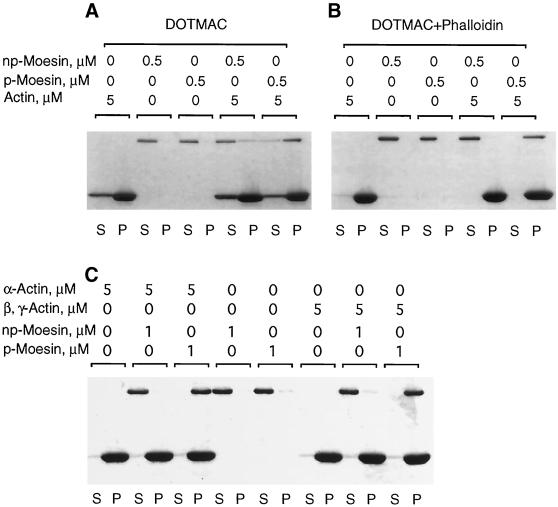
Figure 4.
Phosphorylated moesin selectively co-sediments with F-actin. (A) Purified phosphorylated (p-) or nonphosphorylated (np-) platelet moesin (0.5 μM) was incubated either alone or together with rabbit skeletal α-F-actin (5 μM) in DOTMAC-containing buffer for 1 h at 25°C before centrifugation, as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Equal volumes of supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions were analysed by SDS-PAGE, and proteins were visualized by Coomassie brilliant blue staining. The top band corresponds to moesin; the bottom band is actin. In the absence of actin, all of the moesin remains in the supernatant. Mixed with F-actin, a large fraction of p-moesin, but only a small fraction of np-moesin, co-sediments and appears in the pellet fraction. As can be seen, a fraction of actin remains in the supernatant, presumably because of a DOTMAC-induced increase in critical concentration for actin polymerization. When phalloidin is added to stabilize F-actin, essentially all of the actin is pelleted; p-moesin, but not np-moesin co-sediments with these phalloidin-stabilized filaments (B). (C) Under identical co-sedimentation conditions, p-moesin sediments equally well with skeletal muscle α- and platelet β, γ-actin.