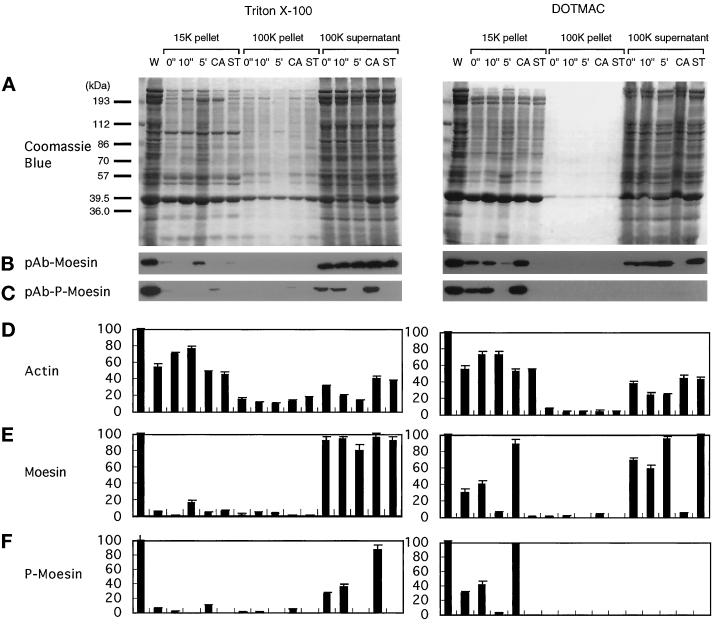
Figure 6.
Phosphorylation-dependent association of moesin with the DOTMAC-insoluble cytoskeleton in thrombin-activated platelets. Platelets were lysed with Triton X-100 (left panels) or DOTMAC (right panels) lysis buffer at the indicated times (0 and 10 s and 5 min) after stimulation with 1 NIH unit/ml human thrombin at 37°C. Platelets were also incubated with 100 nM calyculin A (CA) or 1 μM staurosporine (ST) for 10 min before thrombin activation for 10 min. Lysates were centrifuged for 4 min at 15,600 × g, and the first supernatants were centrifuged for a further 30 min at 100,000 × g. Low- and high-speed pellets and high-speed supernatants were solubilized in SDS sample buffer, and the proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE on a 9% gel and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. (A) Coomassie brilliant blue–stained gels of the Triton X-100 (left) and DOTMAC (right) extraction and fractionation. After transfer of the proteins to nitrocellulose, blots were incubated with polyclonal antibodies to moesin (pAb-moesin; B) or phosphorylated moesin (pAb-p-moesin; C). Relative amounts of actin (D), moesin (E), and phosphorylated moesin (F) were obtained by densitometric analysis of the gels shown in A and the corresponding immunoblots of B and C. The blots shown in B and C are representative of three separate experiments. The data presented in D–E represent the means ± SD of three separate measurements. For detailed description and explanation, see text.