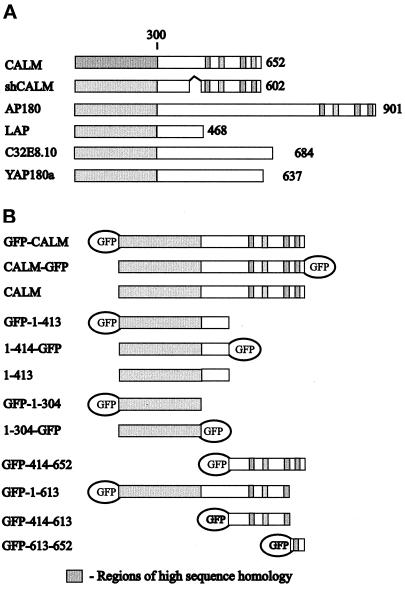
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of CALM and homologous proteins. (A) Depicted are the full-length and the short-form human CALM (shCALM; 50 residues are deleted), rat AP180, Drosophila melanogaster LAP, Caenorhabditis elegans C32E8.10 (U88308), and yeast yAP180A. The approximate positions of the regions with the highest sequence similarity between proteins, corresponding to the CALM amino acid residues 1–300, 507–533, 539–553, 567–590, and 623–638, and the internal deletion of residues 420–469 (marked with ∧) because of the alternative splicing of human CALM are indicated. The number to the right of each lane represents the total number of residues. (B) The fragments of CALM expressed as GFP fusion proteins are shown. The first and the last CALM residues and the position of the GFP moiety are indicated for each construct. Fragments 1–413 and 414–652 as well as the full-length CALM were also expressed as GST fusion proteins.