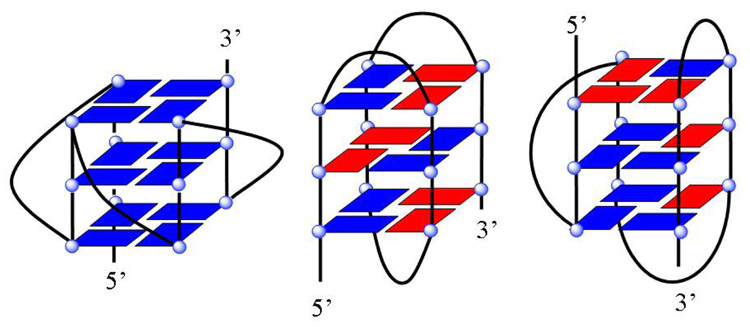
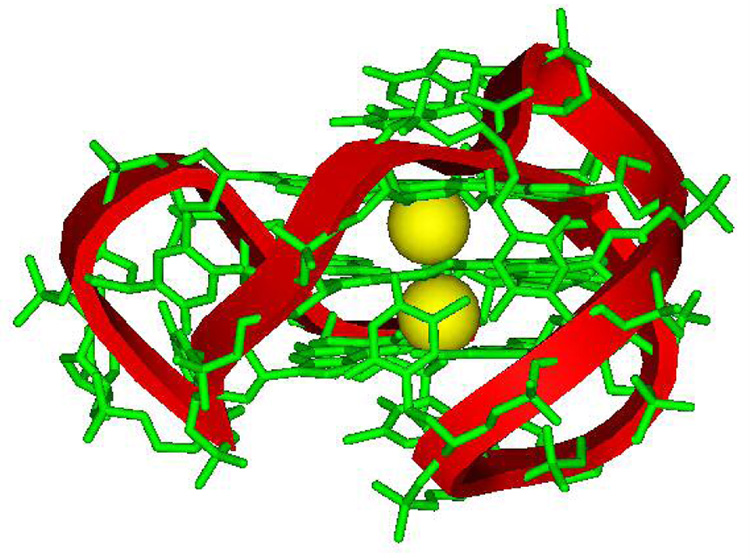
Figure 2.
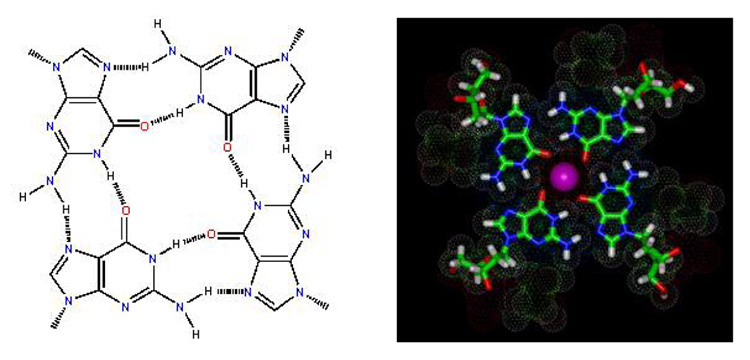
a) H-bonded, four-G stacking unit of quadruplexes: in the model on the right, a K+ ion can be seen (pink) coordinated to the G carbonyl oxygens (red) that point to the center of the four-G tetramer unit that forms the core structure of G4 DNA quadruplexes. Other atoms in the model are green, C; blue, N; and white, H. b) Possible folding models for the human telomere G4 DNA structure. The G bases in the G4 units can be either anti (blue) or syn (red) as shown for a parallel (left) or propeller, a basket (center), or hybrid (right) conformation. c) Molecular model of a human telomere hybrid structure (5) with bases in green, backbone sugars and phosphate shown as a ribbon, and coordinated K+ as yellow spheres. The model is for the major human telomere conformation found in the mix of species in K+ solution (2, 3, 5–9).