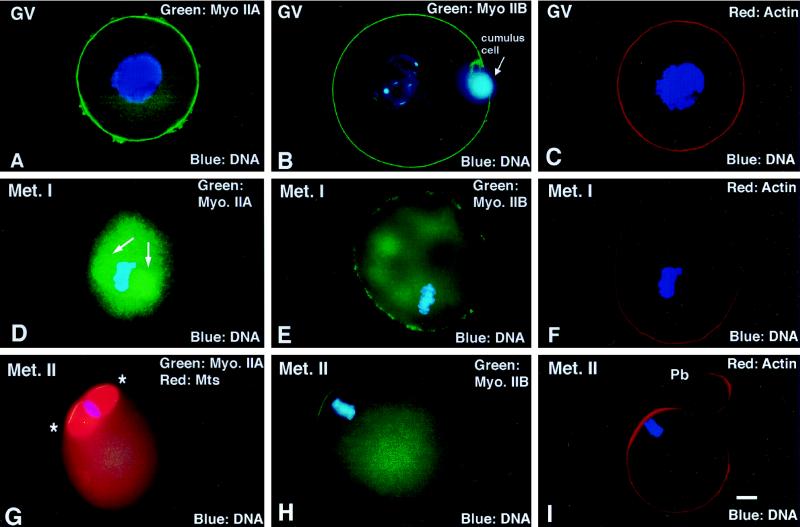
Figure 2.
Detection of myosin IIA and IIB isotypes during meiotic maturation and in the unfertilized oocyte arrested at second meiotic metaphase. (A–C) In immature GV stage oocytes, myosin IIA, myosin IIB, and actin are uniform in the cortex. (D–F) By the first meiotic metaphase, myosin IIA decreases in the cortical region and increases in the cytoplasm, associating prominently with the metaphase spindle (D, arrows). Myosin IIB is discontinuous in the cortex and detected within the cytoplasm, but no association with the meiotic spindle or chromosomes is observed. Cortical actin filament detection remains uniform. (G–I). In the unfertilized oocyte, myosins IIA and IIB as well as actin filaments are enhanced in the region overlying the metaphase-arrested second meiotic spindle (G, ∗, second meiotic spindle region). (A, C, D, and F) Triple-labeled images for myosin IIA (green), actin (red), and DNA (blue). (B, E, and H) Double labeled for myosin IIB (green) and DNA (blue). (G) Triple labeled for myosin IIA (green), microtubules (red), and DNA (blue). (I) Double labeled for actin (red) and DNA (blue). Bar, 10 μm.