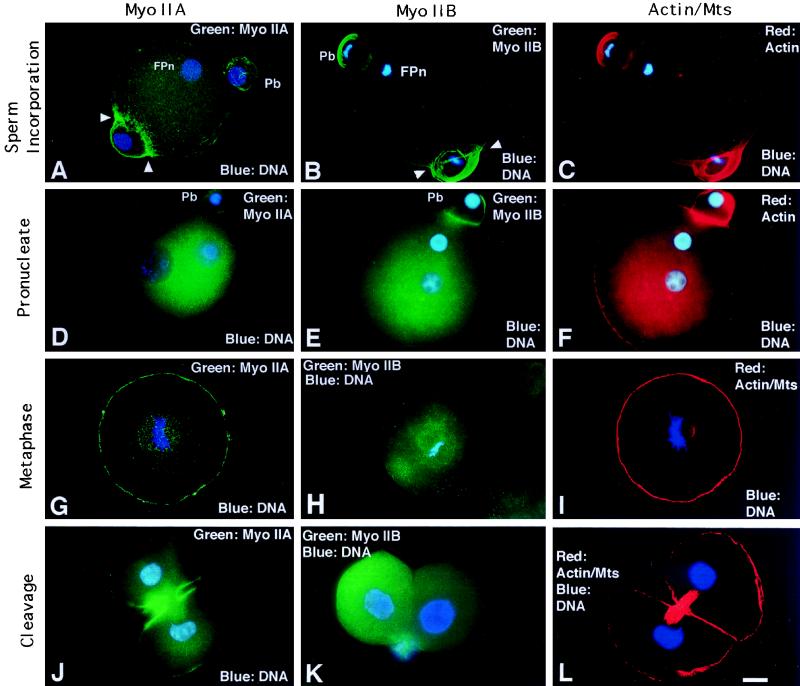
Figure 5.
Myosin IIA and IIB localization during sperm incorporation and first mitosis. (A–C) Myosin IIA (A), IIB (B), and actin (C) assemble in the second polar bodies (Pb) and the sperm incorporation cones, where both isoforms ensheathe the sperm penetration site (A and B, arrowheads). (D–F) In early interphase oocytes, cytoplasmic myosin IIA (D) and IIB (E) increases as cortical detection decreases, except in the region of the second polar body (Pb). Cortical actin staining remains uniform (F). (G–I) At first mitotic metaphase, cortical and spindle-associated myosin IIA staining is prominent (G). Myosin IIB appears diffuse in the cytoplasm, is absent cortically, and is not detected in the mitotic spindle (H). Actin filaments remain uniform in the cortex (I, spindle poles colabeled with acetylated α-tubulin antibody). (J) In telophase zygotes, myosin IIA strongly localizes to the cleavage furrow and opposing plasma membranes of daughter blastomeres; the midbody is weakly detected. (K) Assembly of myosin IIB is not detected in cleaving zygotes or daughter cells following division. (L) A newly formed two-cell embryo double labeled for microfilaments with antiactin antibody and for midbody microtubules with acetylated α-tubulin antibody. (A, D, G, I, J, and L) Quadrupled labeled for myosin IIA (green), actin, acetylated α-tubulin (red), and DNA (blue). (B, C, E, F, and H) Double labeled for myosin IIB (green) and DNA (blue). (K) Double labeled for myosin IIB (green) and DNA (blue). Fpn, female pronucleus; Pb, second polar body. Confocal images: A, B, C, G, I, and L. Epifluorescence: D, E, F, H, J, and K. Bar, 10 μm.