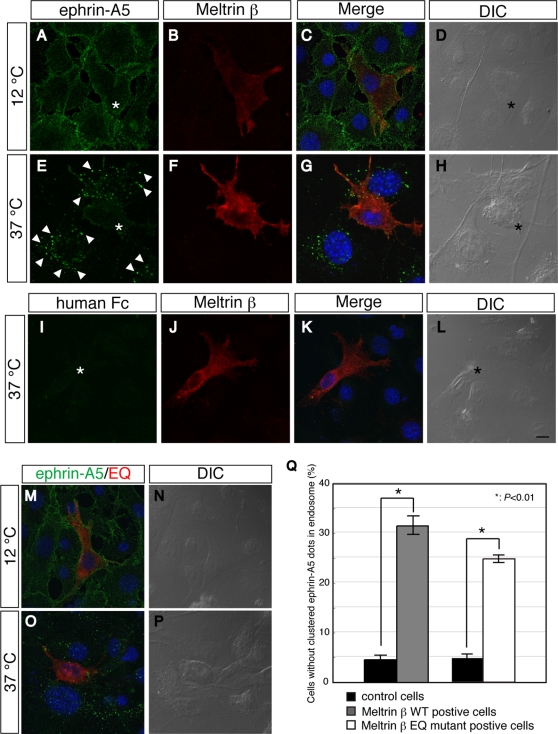
Figure 6. Meltrin β regulates vesicular internalization of the ephrin-A5–EphA4 complexes.
(A–L) Ephrin-A5-Fc fusion proteins bound to EphA4-HA transformants equally regardless of Meltrin β expression at a temperature that inhibits endocytosis (12°C; A–D). In contrast, when the cells were put at a temperature that promotes endocytosis (37°C), Meltrin β substantially inhibited endocytosis of ephrin–Eph complexes (E–H, arrowheads: intracellular vesicles containing ephrin-Eph complexes). Control human Fc fragments do not promote endocytosis (I–L). Asterisk: Meltrin β positive cells. Blue signals in panels C, G, and K are DAPI staining of nuclei. Bar: 10 µm. (M–P) The same experiments were performed for Meltrin β EQ mutant–expressing cells. EQ mutant proteins also inhibit internalization of ephrin–Eph complexes. (Q) The number of the cells that did not have intracellular vesicles containing ephrin–Eph complexes was counted. The number of cells without endosomes containing ephrin–Eph complexes was approximately 7 times or 5 times higher in the Meltrin β WT–positive cells or in the Meltrin β EQ mutant–positive cells respectively than in the control cells (P<0.01, Student's t-test).