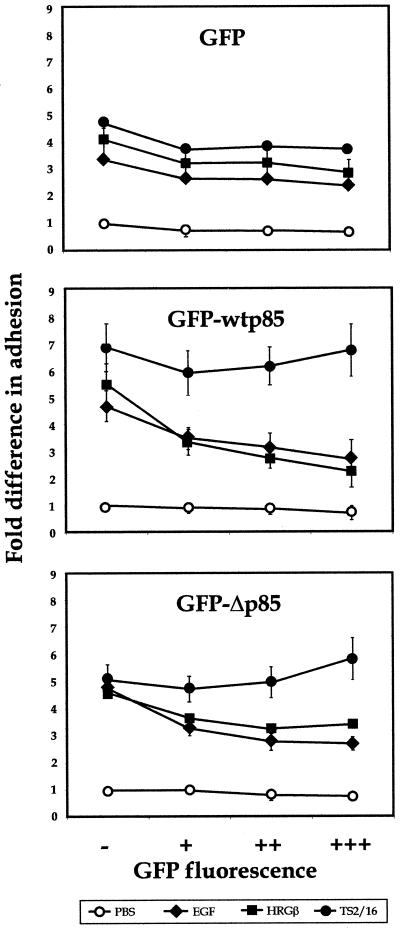
Figure 11.
Overexpression of the wild-type or dominant negative p85 subunit of PI 3-K inhibits EGF- or HRGβ-mediated increases in MDA-MB-435 adhesion to COLL. Control vector expressing GFP (top panel) or constructs expressing a GFP-wt p85 (middle panel) or GFP-Δp85 (bottom panel) fusion protein were transiently transfected into MDA-MB-435 cells as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Transfected cells were allowed to recover for 24 h and then placed in serum-free media overnight. Cells were harvested as for standard adhesion assays, except that no Calcein AM labeling was performed, and cells (∼300,000 cells per well) were added to 24-well plates coated with 6 μg/well COLL. Adhesion was analyzed in the presence of PBS alone (open circles) or containing 1 μg/well TS2/16 (solid circles), 100 ng/ml EGF (solid diamonds), or 100 ng/ml HRGβ (solid squares) for 10 min at 37°C. Nonadherent cells were washed away, and adherent cells were collected fromwells using a 1:1 trypsin:1 mM EDTA solution. Collected cells were then analyzed by flow cytometry using aliquots of preadherent cell populations to confirm cell numbers added to wells for each transfectant and to determine the percent expression of GFP in the starting cell populations. Percent adhesion was determined by gating GFP-negative (−), GFP-low (+), -middle- (++), and -high (+++)-positive cells and comparing preadherent and adherent cell numbers from each population. The data shown reflect fold differences in adhesion when compared with the GFP-negative, unstimulated cell subpopulation from each transfectant. Average percent adhesion was determined from samples examined in triplicate for each stimulation condition, and results were similar for a minimum of three independent assays.