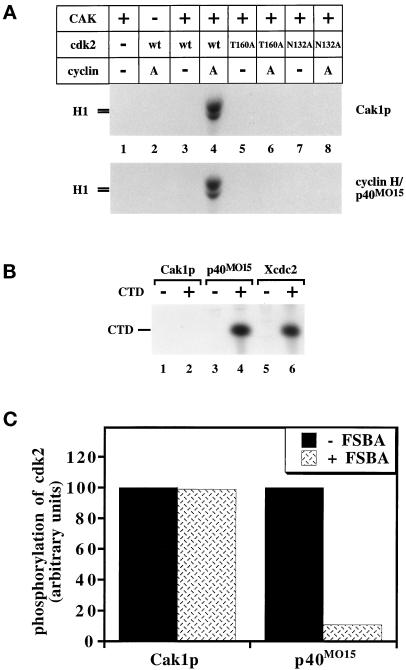
Figure 1.
Basic properties of yeast and human CAKs. (A) The activation of wild-type cdk2 expressed in insect cells and of mutant forms of cdk2 expressed in bacteria by CAK in the presence or absence of cyclin A173–432 was monitored by the ability of cdk2 to phosphorylate histone H1. The T160A mutation alters the site of activating phosphorylation, whereas the N132A mutation renders cdk2 catalytically inactive. (B) Phosphorylation of the CTD peptide by GST-Cak1p (lanes 1 and 2), p40MO15/cyclin H (lanes 3 and 4), and Xenopus cdc2/cyclin B complexes (lanes 5 and 6). The CTD peptide was present in the even-numbered lanes. The same amounts of Cak1p and of p40MO15 were used as in panel A. (C) GST-Cak1p or p40MO15/cyclin H was preincubated with the irreversible inhibitory ATP-analog 5′-p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyladenosine (FSBA) before assaying for phosphorylation of cdk2/cyclin A173–432 (mass ratio, 1:0.75). As a control, FSBA was inactivated by incubation with DTT before addition to CAK (−FSBA lanes). Lanes represent the averages of three and five measurements for GST-Cak1p and p40MO15/cyclin H, respectively.