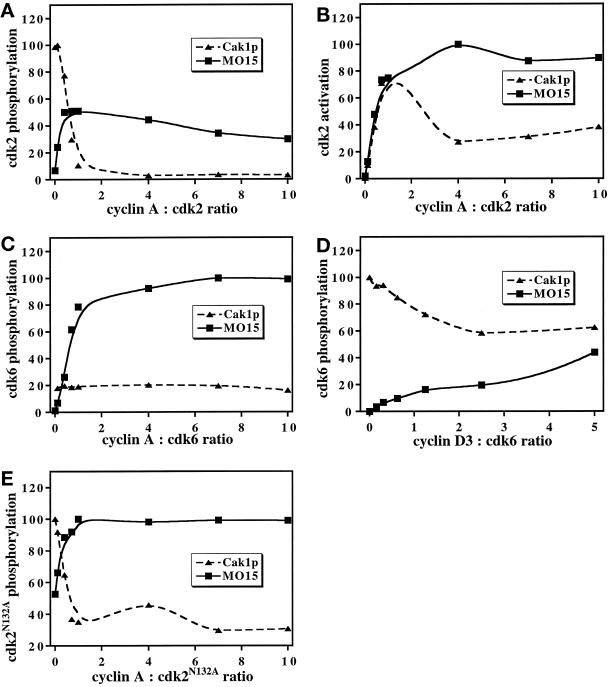
Figure 3.
Effect of cyclins on phosphorylation of cdks by Cak1p and p40MO15/cyclin H. Phosphorylation (A) and activation (B, measured as the phosphorylation of histone H1 by cdk2) of wild-type cdk2 or phosphorylation of cdk2N132A (E) by GST-Cak1p (triangles) and by p40MO15/cyclin H (squares) were determined in the presence of increasing concentrations of cyclin A173–432. Phosphorylation of cdk6 expressed in insect cells was analyzed in a similar manner in the presence of various concentrations of cyclin A173–432 (C), which binds cdk6 very weakly, or of His6-cyclin D3 (D). Note that His6-cyclin D3 binds less tightly to cdk6 in vitro (Kato et al., 1994a) than does cyclin A173–432 to cdk2, resulting in less pronounced effects on cdk phosphorylation. Data were analyzed by phosphorimaging and are expressed in arbitrary units. The cyclin:cdk ratios are mass ratios of the indicated proteins.