Abstract
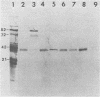
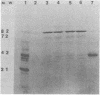
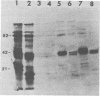
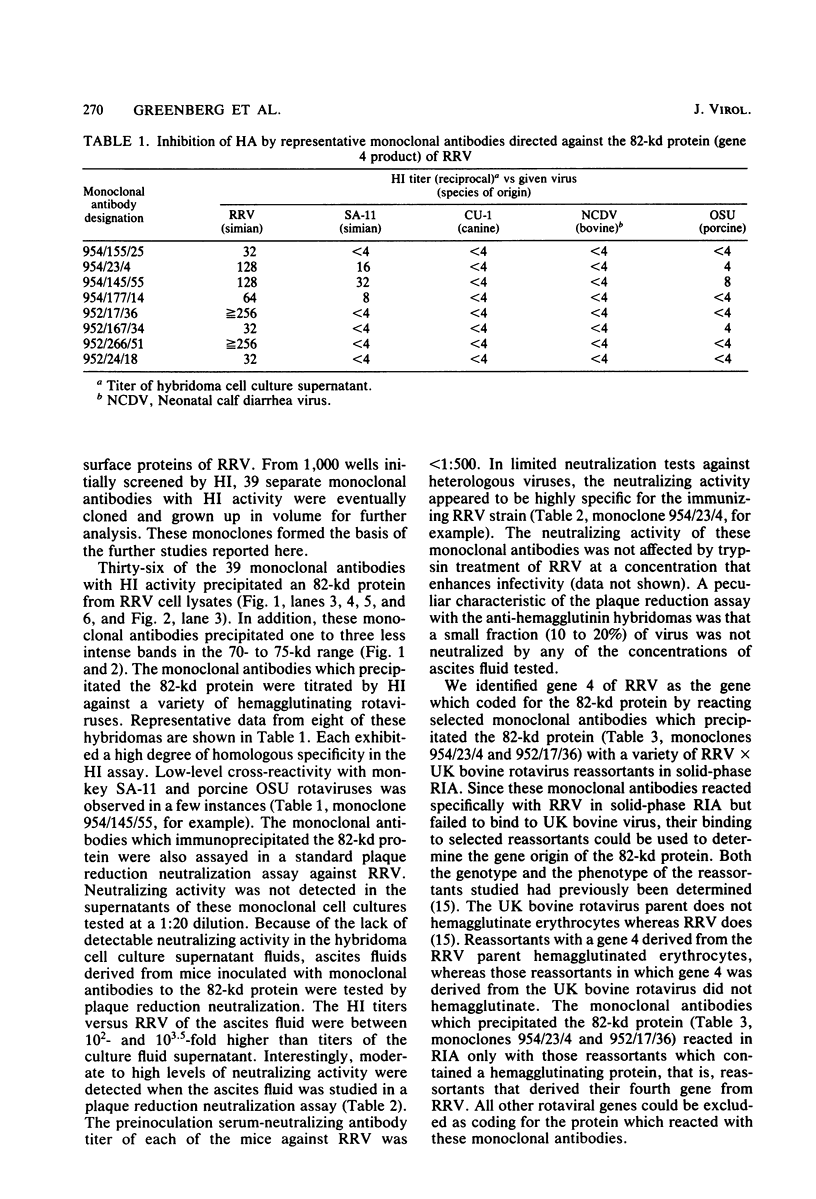
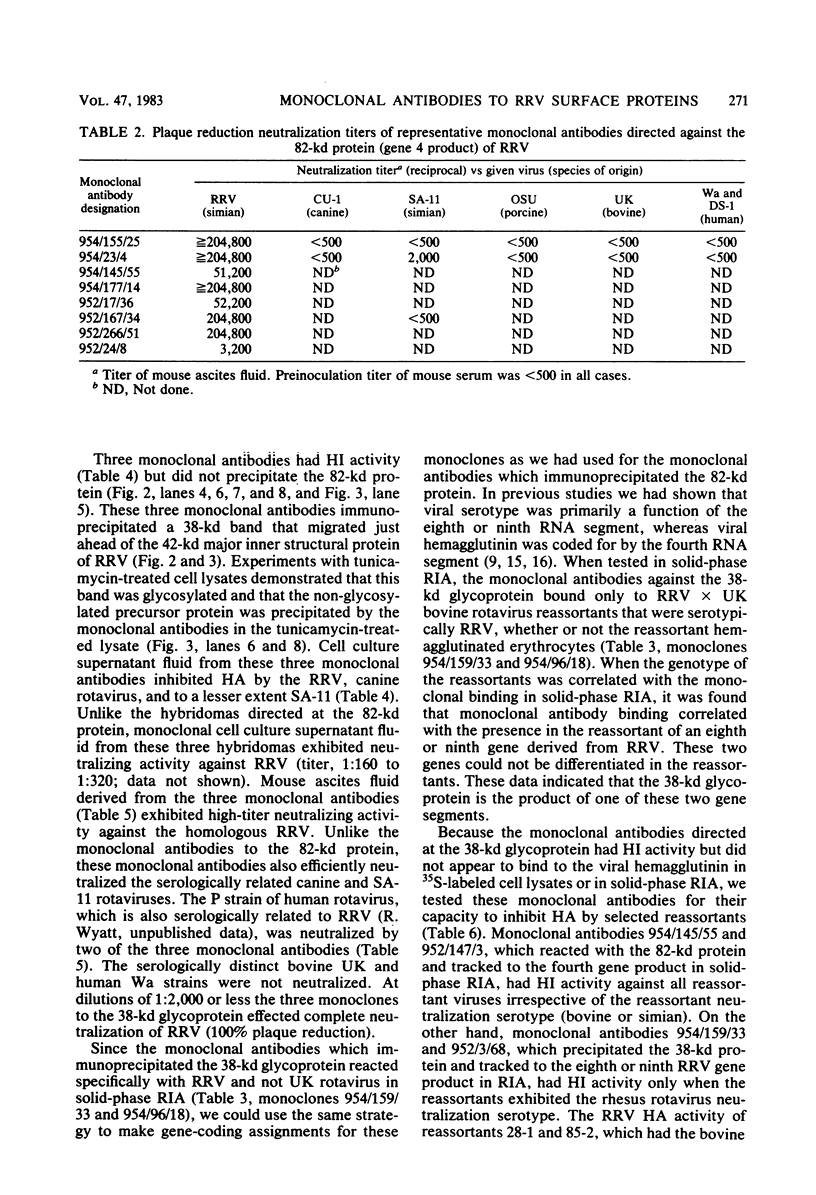
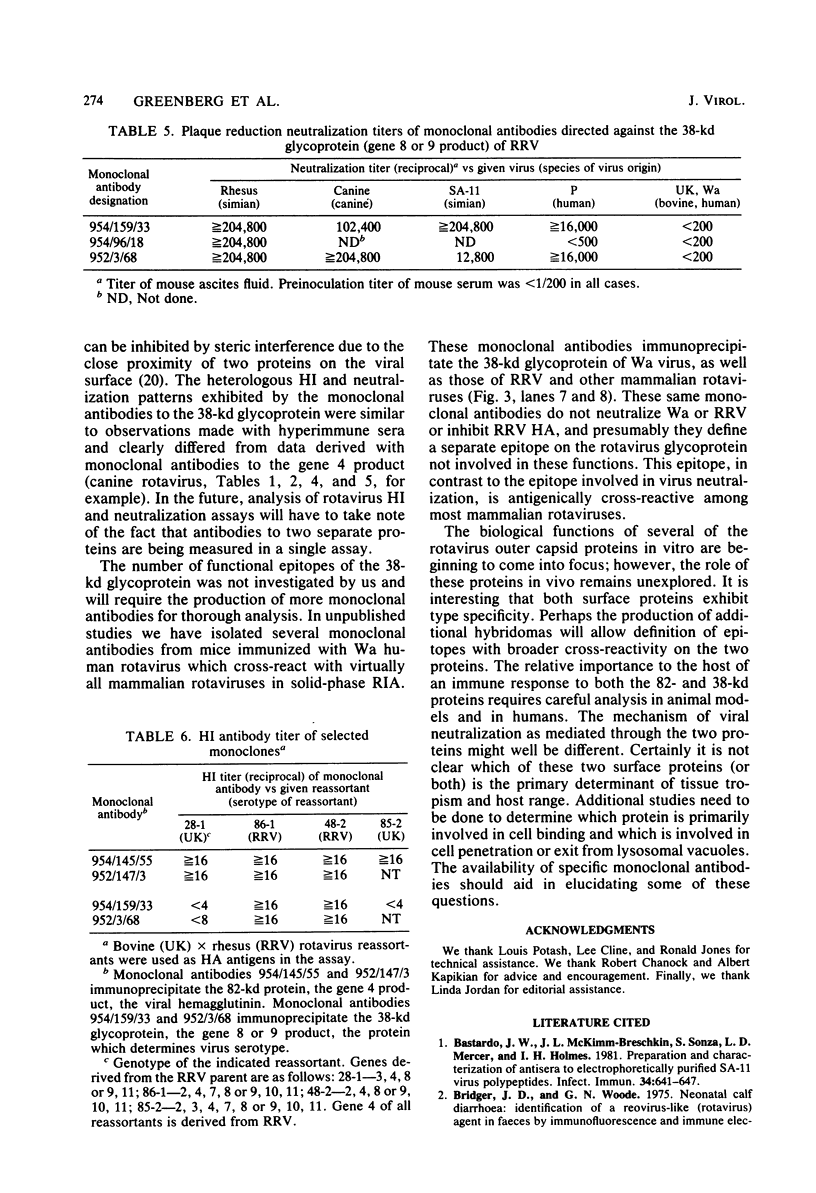
A series of monoclonal antibodies was isolated which reacted with one of two major surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. Thirty-six monoclonal antibodies immunoprecipitated the 82-kilodalton outer capsid protein, the product of the fourth gene, the viral hemagglutinin. These monoclonal antibodies exhibited hemagglutination inhibition activity and neutralized rhesus rotavirus to moderate or high titer. Three monoclonal antibodies immunoprecipitated the 38-kilodalton outer capsid glycoprotein, the eighth or ninth gene product. These three monoclonal antibodies neutralized rhesus rotavirus to high titer and also inhibited viral hemagglutination.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastardo J. W., McKimm-Breschkin J. L., Sonza S., Mercer L. D., Holmes I. H. Preparation and characterization of antisera to electrophoretically purified SA11 virus polypeptides. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):641–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.641-647.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Woode G. N. Neonatal calf diarrhoea: identification of a reovirus-like (rotavirus) agent in faeces by immunofluorescence and immune electron microscopy. Br Vet J. 1975 Sep-Oct;131(5):528–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstin S. J., Spriggs D. R., Fields B. N. Evidence for functional domains on the reovirus type 3 hemagglutinin. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):146–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90514-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. Ribonucleic acid polymerase activity associated with purified calf rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Sep;36(3):395–402. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., López S., Arias C. Structural polypeptides of simian rotavirus SA11 and the effect of trypsin. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):156–160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.156-160.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Mason B. B. Proteolytic enhancement of rotavirus infectivity: molecular mechanisms. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):879–888. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.879-888.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Greenberg H. B., Myslinski J., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Use of transcription probes for genotyping rotavirus reassortants. Virology. 1982 Sep;121(2):288–295. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Jones R. Gene coding assignments for growth restriction, neutralization and subgroup specificities of the W and DS-1 strains of human rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):313–320. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Jones R. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Rescue of noncultivatable human rotavirus by gene reassortment during mixed infection with ts mutants of a cultivatable bovine rotavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):420–424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Jones R. Rescue and serotypic characterization of noncultivable human rotavirus by gene reassortment. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):104–109. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.104-109.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H., McAuliffe V., Valdesuso J., Wyatt R., Flores J., Kalica A., Hoshino Y., Singh N. Serological analysis of the subgroup protein of rotavirus, using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.91-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes E. C., Lee P. W., Miller S. E., Joklik W. K. The interaction of a series of hybridoma IgGs with reovirus particles. Demonstration that the core protein lambda 2 is exposed on the particle surface. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90534-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Scott F. W., Appel M. J. Isolation and characterization of a canine rotavirus. Arch Virol. 1982;72(1-2):113–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01314456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Flores J., Greenberg H. B. Identification of the rotaviral gene that codes for hemagglutination and protease-enhanced plaque formation. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):194–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Flores J., Sereno M. M., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genes of human (strain Wa) and bovine (strain UK) rotaviruses that code for neutralization and subgroup antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., James J. D., Jr, Kapikian A. Z. Hemagglutination by simian rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Mar;7(3):314–315. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.3.314-315.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killen H. M., Dimmock N. J. Identification of a neutralization-specific antigen of a calf rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Oct;62(Pt 2):297–311. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-2-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolbourne E. D. Recombination of influenza A viruses of human and animal origin. Science. 1968 Apr 5;160(3823):74–76. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3823.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Hayes E. C., Joklik W. K. Characterization of anti-reovirus immunoglobulins secreted by cloned hybridoma cell lines. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):134–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90533-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason B. B., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. In vitro transcription and translation of simian rotavirus SA11 gene products. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1111–1121. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1111-1121.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Inouye S. Purification of an outer capsid glycoprotein of neonatal calf diarrhea virus and preparation of its antisera. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):155–158. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.155-158.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., McCorquodale J. G. The molecular biology of rotaviruses. II. Identification of the protein-coding assignments of calf rotavirus genome RNA species. Virology. 1982 Mar;117(2):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90482-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Alter H. J., Holland P. V. Microtiter solid-phase radioimmunoassay for hepatitis B antigen. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):478–484. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.478-484.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Lazdins I., Holmes I. H. Coding assignments of double-stranded RNA segments of SA 11 rotavirus established by in vitro translation. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):976–982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.976-982.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs D. R., Fields B. N. Attenuated reovirus type 3 strains generated by selection of haemagglutinin antigenic variants. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):68–70. doi: 10.1038/297068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuker G., Oshiro L. S., Schmidt N. J. Antigenic comparisons of two new rotaviruses from rhesus monkeys. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):202–203. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.202-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Bohl E. H., Cross R. F., Kohler E. M., Agnes A. G. Pathogenesis of porcine rotaviral infection in experimentally inoculated gnotobiotic pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Feb;39(2):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., James W. D., Pittman A. L., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Definition of human rotavirus serotypes by plaque reduction assay. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):110–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.110-115.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Barbour B., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for identification of rotaviruses from different animal species. Science. 1978 Jul 21;201(4352):259–262. doi: 10.1126/science.208150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]