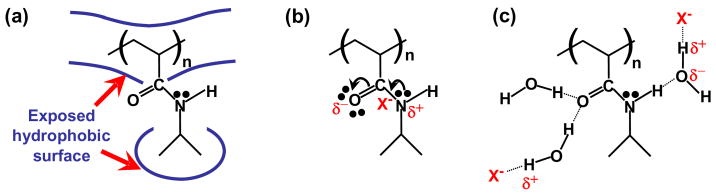
Figure 1.
Three basic interactions amongst anions, PNIPAM, and hydration waters are involved in the Hofmeister effect: (a) The hydrophobic hydration of the molecule is associated with surface tension and can be modulated by salt; (b) Direct binding of the anion to the amide group of PNIPAM; (c) Hydrogen bonding of the amide and its destabilization through polarization by the anion, X−.