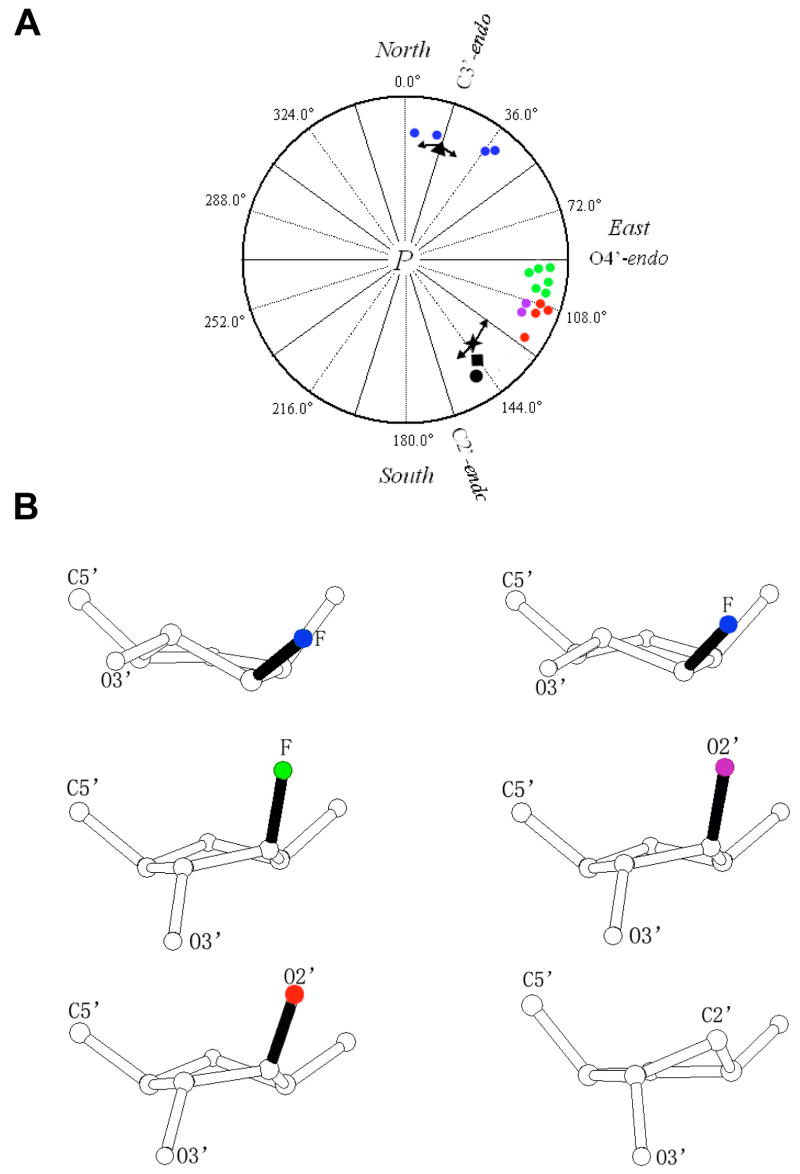
FIGURE 4.
Conformational properties of ANA and FANA nucleosides. (A) Pseudorotation phase angles P for FANA and ANA sugars in the A-form and B-form duplexes with reference values for DNA:RNA hybrids and canonical A-RNA and B-DNA duplexes. The phase angle is defined as tan P = [(ν4-ν1)–(ν3+ν0)]/[2ν2(sin36° + sin72°)], where ν0 to ν4 are the endocyclic torsion angles of the pentofuranose (ν0 O4′-C1′, ν1 C1′-C2′, ν2 C2′-C3′, ν3 C3′-C4′, ν4 C4′-O4′) (60). The color code is as follows: A-FANA1 and A-FANA2, blue circles; B-FANA, green circles (19); A-ANA, purple circles; B-ANA1 and B-ANA2, red circles; P angle ranges in the native A-DNA decamer (all residues) and B-DNA dodecamer duplexes (thymidines) are shown with arrows and average values are marked by a black triangle and cross, respectively (for a recent overview of P angle ranges in A- and B-form duplexes see (66)); average puckers of DNA residues in the crystals of complexes between DNA:RNA hybrids and HIV-I RT (33) and bacterial RNase H (36), black circle and square, respectively. (B) Examples of sugar conformations observed in the crystal structures of FANA-and ANA-modified DNA duplexes. The color code for 2′-substituents matches that in panel A. Top left: C3′-endo FANA (A-FANA1 residue faT6); top right: C4′-exo FANA (A-FANA2 residue faT36); middle left: O4′-endo B-FANA (19); middle right: C1′-exo A-ANA (residue aU6); bottom left: C1′-exo B-ANA1 (residue aU7); bottom right: DNA C2′-endo (reference).