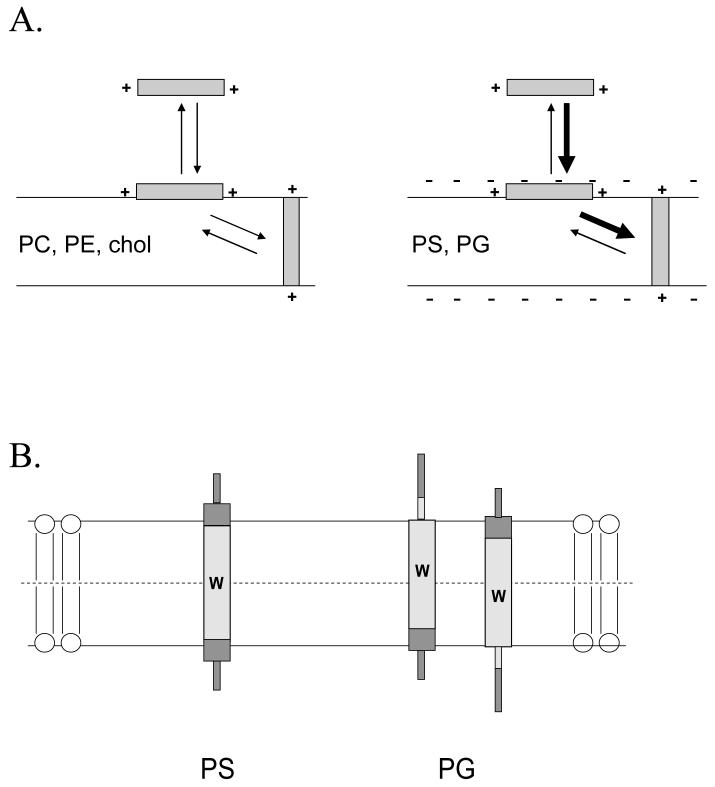
Figure 8.
Schematic illustration of the proposed difference in peptide topography in DOPG and DOPS-containing vesicles. (A) Effect of anionic lipid on membrane association and topographical equilibria. Notice that anionic lipid enhances both binding of polypeptides to membrane and the formation of the TM topography when the polypeptide is membrane-bound. (B) Difference between topography in DOPG and DOPS vesicles. Trp location is indicated by the “W”. The hydrophobic core of the peptide is shown by light gray shading and the hydrophilic flanking segments by dark gray shading. Helical sequences are indicated by thick rectangular regions and disordered sequences by thin rectangular regions. In addition to the topographical difference illustrated here may be a lesser degree of formation of the TM topography in the presence of DOPG-containing vesicles.