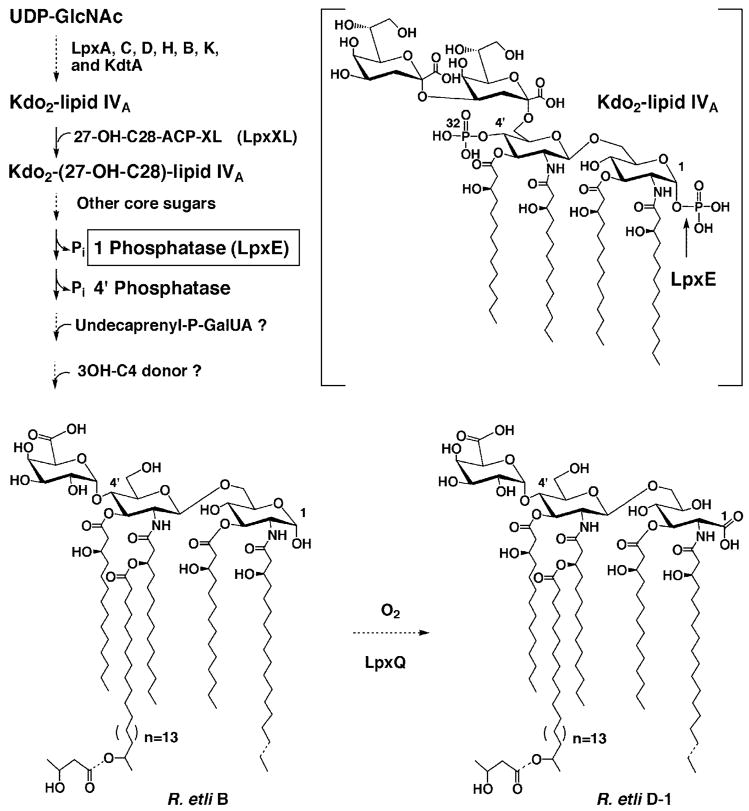
Fig. 1. Structure and biosynthesis of lipid A molecules in R. etli CE3.
The major lipid A species B and D-1 (16, 17, 114) contain no phosphate moieties in R. etli or R. leguminosarum. However, the seven enzymes that make Kdo2-lipid IVA in E. coli are also found in extracts of R. leguminosarum and R. etli (37). With the possible exception of lpxH (3, 115), the genes encoding these enzymes are present in single copy. Although very active with the model substrate Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA (structure in brackets), the LpxE phosphatase (cleavage site indicated by arrow) does not require the Kdo moiety for activity. However, LpxE normally functions after the secondary acyl chain and additional core sugars have been added (39) and is predicted to have a periplasmic active site. Most of the other enzymes needed to generate component B have previously been identified in R. leguminosarum and R. etli (22,37–39,43) with the exception of those that incorporate the 4′-galacturonic acid and β-hydroxybutyrate residues. Following the formation of component B and transport to the outer membrane, the LpxQ oxidase (43, 44) converts the proximal glucosamine residue to the 2-aminogluconate unit in an oxygen dependent manner to generate D-1. Both B and D-1 may also be 3-O-deacylated to form the minor components C and E (not shown) respectively.