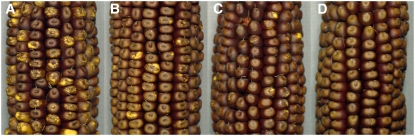
Figure 6.
Ears Illustrating the Genetic Assay for 9S Chromosome Breakage Activity.
bz-s derivatives (C bz-s/C sh-bz-X2) were crossed as pollen parents to c testers (c Bz). Breaks occurring during endosperm development are visualized as colorless (acyanic) sectors arising from the loss of the dominant C marker located distal to Bz in 9S. The phenotype of kernels receiving the sh-bz-X2 chromosome (∼45% due to its reduced male transmission) is solid color; that of kernels receiving the bz-s derivative chromosome is either mosaic or solid. Breakage activity is expressed as percentage of mosaic (BFB) kernels among those receiving a bz-s chromosome.
(A) bz-s derivative H74.2 (class 8, ITS deletion, adjacent inversion; 95.3% BFB).
(B) bz-s derivative H95.1 (class 9, MTn transposition; 82.4% BFB).
(C) bz-s derivative H3.12 (class 8, ITS deletion, adjacent inversion; 26.5% BFB).
(D) bz-s derivative H90.1 (class 10, MTn excision; 0% BFB).